- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
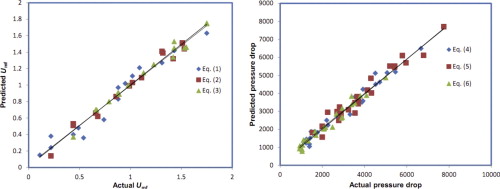
• Statistical modeling correlated ΔP and Umf with operating parameters in a three-stage fluidizer.
• Model-predicted values of ΔP and Umf fitted well the experimental data.
• Umf in the top bed of a three-stage system was less than that in an identical single-stage bed.
• Total ΔP over the three-stage fluidized bed was less than that of an identical single-stage bed.
The present paper describes the statistical modeling and optimization of a multistage gas–solid fluidized bed reactor for the control of hazardous pollutants in flue gas. In this work, we study the hydrodynamics of the pressure drop and minimum fluidization velocity. The hydrodynamics of a three-stage fluidized bed are then compared with those for a single-stage unit. It is observed that the total pressure drop over all stages of the three-stage fluidized bed is less than that of an identical single-stage system. However, the minimum fluidization velocity is higher in the single-stage unit. Under identical conditions, the minimum fluidization velocity is highest in the top bed, and lowest in the bottom bed. This signifies that the behavior of solids changes from a well-mixed flow to a plug-flow, with intermediate behavior in the middle bed.