- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
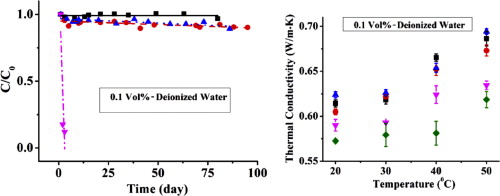
• CNTs were functionalized via refluxing to lessen their lengths and improve dispersion stability.
• The nanofluids prepared using functionalized CNTs can keep stable for more than 80 days.
• Thermal conductivity of nanofluids prepared using refluxed CNTs was higher than unrefluxed ones.
• Thermal conductivity of the prepared nanofluids increased with increasing the temperature.
Water-based nanofluids were prepared with multi walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) of different lengths in concentrations of 0.1, 0.25 and 0.5 vol%. To improve their dispersibility, pristine MWCNTs were functionalized and cut into small lengths by reflux in an oxidizing mixture of 3:1 sulfuric and nitric acids. The initial length of the carbon nanotubes (CNTs; 10–15 μm) was reduced to 203, 171 and 134 nm after 1, 2 and 4 h of reflux, respectively. Surface modification and the reduced length of the CNTs, improved the stability of the nanofluids with no significant sedimentation observed after 80 days. Furthermore, the thermal conductivities of nanofluids prepared using refluxed CNTs, were higher than that of the pristine CNTs. The thermal conductivity also increased with the nanofluid temperature. The nanofluid prepared with 1 h refluxed CNTs had the highest thermal conductivity. The enhanced thermal conductivity and stability of the nanofluids was attributed to the decreased length of CNTs.