- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
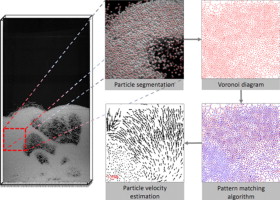
• High-speed imaging was coupled with segmentation and Voronoi method to acquire particle velocities.
• Thousands of particles could be tracked at the same time in a 2D fluidized bed.
• Solid volume fraction and granular temperature can be derived from Lagrangian particle description.
• Solid phase velocity field could be reconstructed from instantaneous particle velocities.
The experimental characterization of particle dynamics in fluidized beds is of great importance in fostering an understanding of solid phase motion and its effect on particle properties in granulation processes. Commonly used techniques such as particle image velocimetry rely on the cross-correlation of illumination intensity and averaging procedures. It is not possible to obtain single particle velocities with such techniques. Moreover, the estimated velocities may not accurately represent the local particle velocities in regions with high velocity gradients. Consequently, there is a need for devices and methods that are capable of acquiring individual particle velocities. This paper describes how particle tracking velocimetry can be adapted to dense particulate flows. The approach presented in this paper couples high-speed imaging with an innovative segmentation algorithm for particle detection, and employs the Voronoi method to solve the assignment problem usually encountered in densely seeded flows. Lagrangian particle tracks are obtained as primary information, and these serve as the basis for calculating sophisticated quantities such as the solid-phase flow field, granular temperature, and solid volume fraction. We show that the consistency of individual trajectories is sufficient to recognize collision events.