- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
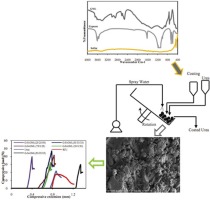
• Urea coating using gypsum, sulfur and GML as coating materials and polyols as sealant was studied.
• Coating formulation of 50% gypsum and 50% GML and with 1.1% polyols was found to be optimum.
• The coated urea with optimal formulation could increase urea release resistance by 34.2%.
The use of urea and urea-based fertilizers has increased considerably over the past 15 years. They currently account for approximately 51% of the world's agricultural nitrogen consumption. However, about 20–70% of the applied urea fertilizer is lost to the environment, causing serious pollution and increasing costs. These losses come from leaching, decomposition, and ammonium volatilization in the soil during handling and storage. Controlled release by coating can be used to increase urea fertilizer efficiency. We studied the use of gypsum, sulfur, and ground magnesium lime as cost-effective coating materials. All these coating materials contain nutrients required by plants. The effects of the coating composition and proportion of sealant on the rate of urea release and the crushing strength of the coated urea were investigated. We found that coated urea with the same proportion of gypsum–ground magnesium lime (GML) exhibited low urea release and high crushing strength. The performance was enhanced when using polyols as a sealant on the surface of the coated urea. A surface morphology analysis indicated a uniform and smooth surface on the coated film. The efficiency of the coated urea improved by 34.2% when using gypsum–GML (1:1 ratio) containing 1.1% polyols.