- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
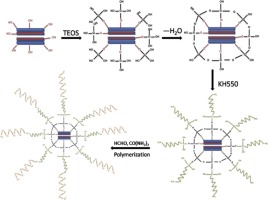
• UF composites containing 20–40 wt% reactive kaolinites were prepared by in situ polymerization.
• The thermal stability of the urea-formaldehyde resin was improved.
• The formaldehyde emission was reduced and water resistance was improved.
Novel urea-formaldehyde resin/reactive kaolinite composites containing 20–40 wt% kaolinite were prepared by in situ polymerization. The kaolinite was modified with tetraethoxysilane and a silane coupling agent to introduce reactive groups. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction confirmed preparation of the urea-formaldehyde resin/reactive kaolinite composites. The composite morphology was investigated using scanning electron microscopy; the composites consisted of uniform spherical particles. The surface chemical components of the composites were determined using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The spectra showed that the reactive kaolinite was encapsulated by the urea-formaldehyde resin. The thermal properties of the composites were examined using differential scanning calorimetry and thermogravimetric analysis. The results showed that their thermal stability was much better than that of pure urea-formaldehyde resin. Reactive kaolinite addition greatly decreased formaldehyde emissions and improved the water resistance of the composites. A mechanism for urea-formaldehyde resin/reactive kaolinite composite synthesis is proposed.