- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
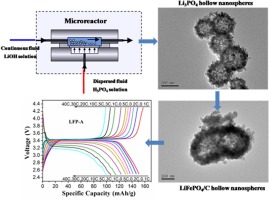
• Li3PO4 hollow nanospheres were synthesized through a micro-dispersion technique.
• The effects of operation parameters on purity and morphology of the product was investigated.
• LiFePO4 hollow nanospheres were synthesized from hollow Li3PO4 via a solvothermal route.
• The synthesized hollow LiFePO4/C nanospheres exhibited good electrochemical performance.
• A possible mechanism for fast formation of hollow structured Li3PO4 was proposed.
Lithium phosphate hollow nanospheres were prepared in a membrane dispersion microreactor using aqueous phosphoric acid and lithium hydroxide solutions as reactants. The influences of reactant flow rate ratio and temperature on the purity and morphology of the prepared nanospheres were investigated using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The results showed that nanospheres prepared in the continuous flow condition had a hollow interior structure with high crystallinity. A possible mechanism for the formation of this hollow structured Li3PO4 was also proposed. Using Li3PO4 hollow nanospheres as the precursor, LiFePO4 hollow nanospheres were successfully synthesized via a solvothermal route in ethylene glycol. After coating with carbon, the LiFePO4/C hollow nanospheres exhibited excellent electrochemical performance, especially at high rates, and could discharge124 mAh/g at 10 C, and even 98 mAh/g at 40 C.