- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
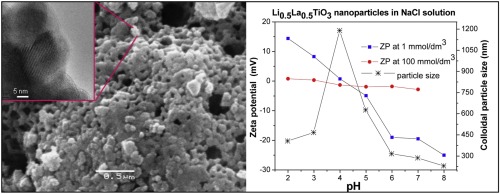
• Zeta potential ζ, isoelectric point IEP and agglomeration of Li0.5La0.5TiO3 colloidal suspensions were studied.
• Zeta potential of Li0.5La0.5TiO3 varied from positive to negative with increasing pH from 2 to 8.
• Li0.5La0.5TiO3 suspensions reached the isoelectric point at pH range of 3–5.
• Li0.5La0.5TiO3 colloidal suspensions were stable in the pH range of 7.0–8.0.
• Li0.5La0.5TiO3 nanoparticles aggregated rapidly at ionic strengths >1 mmol/dm3.
The zeta potential, isoelectric point, and agglomeration of Li0.5La0.5TiO3 (LLTO) nanoparticles dispersed in aqueous media at different ionic strengths have been studied. The zeta potential was determined from electrophoretic mobility measurements, according to Smoluchowski's equation, for Li0.5La0.5TiO3 suspensions in NaCl and KCl electrolytes with ionic strengths of 1, 10, and 100 mmol/dm3. The isoelectric point (IEP), zeta potential (ζ), and the agglomeration were shown to strongly depend on the ionic strength of the Li0.5La0.5TiO3 aqueous colloidal suspension in both NaCl and KCl electrolytes, which allows the determination of the effects of environmental conditions for Li0.5La0.5TiO3 manipulation in aqueous colloidal systems. The suspensions of Li0.5La0.5TiO3 nanoparticles reach the IEP in the pH range of 3–5. The ζ of Li0.5La0.5TiO3 nanoparticles varied from positive to negative values with a pH increase, which allows for the control of the surface charge depending on the purpose. The pH range of 7–8 and an ionic strength ≤1 mmol/dm3 are recommended as the most suitable conditions for both the LLTO colloidal shaping techniques application and the LLTO-based nanocomposite formation.