- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
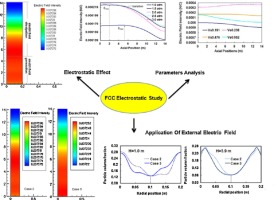
• Electrostatic effect in FCC risers was studied by CFD simulation coupled with electrostatic model.
• The coupled model was verified using open experimental data.
• Simulation results demonstrated obvious electrostatic effects in FCC risers.
• Electrostatic effect in small-scale FCC risers was stronger than their large-scale counterparts.
• External electric field may be applied to tailor the flow field in FCC risers.
A CFD simulation was proposed to investigate the electrostatic effect on the hydrodynamic behavior of turbulent gas–solid flow in FCC risers. The simulation was first verified using the open experimental data with expected electrostatic effects observed in FCC risers. The influences of several operating parameters on the degree of electrification in FCC risers were analyzed, such as surface charge densities, pressure, gas velocity. It was noted that the gas velocity played a highly significant role compared with solid flux, while the effect of pressure was relatively weak. Further analysis showed that a much stronger electrostatic effect was found in small-scale FCC risers than their large-scale counterparts, and in addition, the major regions affected by the electrostatic charge depend on the scale of the riser. Finally, an external electric field was applied to optimize the flow field distribution in the FCC riser. The results of the electrostatic effects on the hydrodynamic behaviors in FCC risers are of great use in providing a reference for the optimization of FCC risers and their scaling.