- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
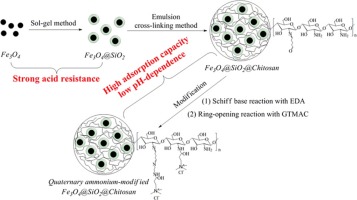
• Chemically modified magnetic chitosan microspheres were prepared and used for Cr(VI) removal.
• Its maximum adsorption capacity was 233.1 mg/g at pH 2.5 and 25 °C.
• The adsorbent exhibited strong acid resistance and a magnetic responsive nature.
• The adsorbent with 95.6% desorption efficiency had a good reusability.
A bioadsorbent composed of magnetic silica nanoparticles encapsulated by chitosan microspheres was prepared by the emulsion cross-linking method, and it was then modified with quaternary ammonium groups by reaction with ethylenediamine and glycidyl trimethylammonium chloride. Characterization of the bioadsorbent indicated that it was highly acid resistant and magnetically responsive. The bioadsorbent was then used to remove Cr(VI) from acidic aqueous solution. The results of batch experiments indicated that the optimal pH value was 2.5, and the adsorbent exhibited low pH dependence. The maximum adsorption capacity was 233.1 mg/g at pH 2.5 and 25 °C, and the equilibrium time was determined to be 40–120 min depending on the initial Cr(VI) concentration. The adsorbent could be effectively regenerated using a mixture of 0.3 mol/L NaOH and 0.3 mol/L NaCl with a desorption efficiency of 95.6%, indicating high reusability. In conclusion, the bioadsorbent shows potential for Cr(VI) removal from acidic wastewater.