- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
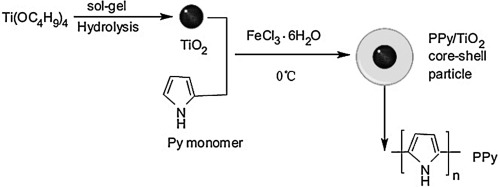
• In situ oxidation polymerization was used to prepare PPy/TiO2 nanocomposites.
• The composites exhibited photocatalytic activity for CO2 reduction.
• The composites were used as photocatalyst for Rhodamine B degradation.
A simple in situ method was developed to synthesize polypyrrole (PPy)/TiO2 nanocomposites having high photocatalytic activity under simulated solar light. The structure and morphology of the PPy/TiO2 nanocomposites were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy, UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The visible light photocatalytic properties of the nanocomposites were demonstrated by Rhodamine B degradation and by the production of methanol from CO2. The XRD analysis showed that the coating of PPy did not change the crystallinity of the TiO2. The UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectra indicated that the light adsorption range of the TiO2 was enlarged after modification. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis confirmed the presence of PPy and TiO2 in the nanocomposite catalyst. The RhB degradation using the nanocomposites was increased by 41% and the methanol yield was enhanced by 34 wt% in comparison with those obtained with pure TiO2. The improvements were considered to originate from the increased separation efficiency of hole–electron pairs from TiO2 and the enhancement of the light adsorption range by the introduced PPy.