- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Thermal stability of oil-filled nanoparticles depends on synthesis conditions.
• Oil release properties were studied by thermo-analytical methods.
• Time- and temperature-dependent oil release profiles were evaluated by FTIR and Raman spectroscopy.
• The kinetics and mechanism of oil release could be described by the Korsmeyer–Peppas model.
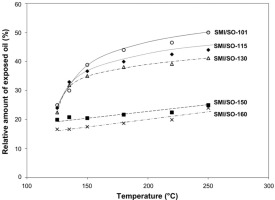
The thermal release properties of soy oil from poly(styrene-co-maleimide) nanoparticles containing 50 wt% encapsulated oil have been quantified as a function of temperature and time. The effects of different synthesis conditions on the thermal stability of the nanoparticles and their oil release have been evaluated, i.e., by gradually increasing the amount of ammonium hydroxide used for the imidization of poly(styrene-co-maleic anhydride). First, the intrinsic thermal properties of the oil-filled nanoparticles were analysed by differential scanning calorimetry, which revealed an exothermal reaction related to the oil release and a suppression of the glass transition that may be masked owing to the complex structure of the hybrid nanoparticles. The isothermal scans showed different rates of oil release after a post-imidization reaction. The oil release was better followed by dynamic mechanical analysis, which illustrated changes in visco-elastic properties expressed by the maximum in the loss factor that related to the amount of released oil. Depending on the amount of ammonium hydroxide, the oil started to release below the glass transition temperature at various rates. Thermal release profiles of the oil were quantified by infrared and Raman spectrocopy after heating for 2 min to 6 h at 125 to 250 °C, based on variations in oil-related and imide-related absorption bands. The oil release increased below and above the glass transition temperature, following a parabolic trend, and progressively decreased at higher ammonium hydroxide concentrations, in parallel with higher imide content and changes in imide conformation. The kinetics and mechanism of the oil release can be described by the Korsmeyer–Peppas model, suggesting a dominating diffusion mechanism that is influenced by further imidization of the polymer matrix during heating.