- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
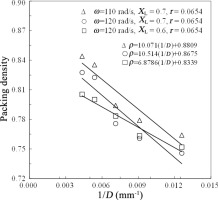
• Packing densification of binary sphere mixtures subjected to 3D mechanical vibrations was studied.
• Influences of various parameters on packing densities were investigated experimentally.
• A highest packing density of ∼0.88 was obtained, in agreement with reported results.
The packing densification of binary spherical mixtures under 3D mechanical vibration was studied experimentally. The influences of vibration frequency (ω), volume fraction of large spheres (XL), sphere size ratio (r, diameter ratio of small to large spheres), and container size (D) on the random binary packing density (ρ) were systematically analyzed. For any given set of conditions, there exist optimal ω and XL to realize the densest random binary packing; too large or small ω and XL is not helpful for densification. The influences of both r and D on ρ are monotonic; either reducing r or increasing D leads to a high value of ρ. With all other parameters held constant, the densest random packing occurs when XL is dominant, which is in good agreement with the Furnas relation. Moreover, the highest random binary packing density obtained in our work agrees well with corresponding numerical and analytical results in the literature.