- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
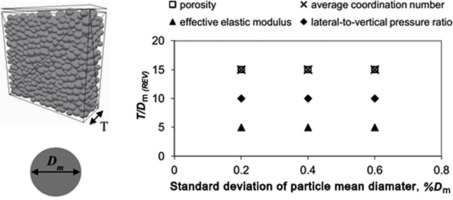
• Minimum representative elementary volume (REV) size for polydisperse granular media was studied.
• Uniaxial compression test was modeled using 3D discrete element method.
• Geometrical and mechanical REVs for sphere packings had different sizes.
• Heterogeneity of granular system had no effect on the REV size.
• Minimum REV size was found to correspond to 15 times particle mean diameter.
The representative elementary volume (REV) for three-dimensional polydisperse granular packings was determined using discrete element method simulations. Granular mixtures of various sizes and particle size distributions were poured into a cuboid chamber and subjected to uniaxial compression. Findings showed that the minimum REV for porosity was larger compared with the REV for parameters such as coordination number, effective elastic modulus, and pressure ratio. The minimum REV for porosity and other parameters was found to equal 15, 10, and 5 times the average grain diameter, respectively. A study of the influence of sample size on energy dissipation in random packing of spheres has also confirmed that the REV size is about 15 times the average grain diameter. The heterogeneity of systems was found to have no effect on the REV for the parameters of interest for the narrow range of coefficient of uniformity analyzed in this paper. As the REV approach is commonly applied in both experimental and numerical studies, determining minimum REV size for polydisperse granular packings remains a crucial issue.