- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
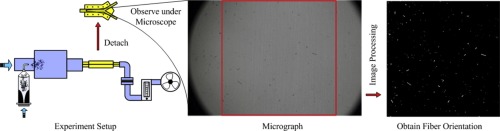
• Fiber deposition experiments were carried out in a single-bifurcation airway model.
• Deposition fractions and orientation under effects of impaction and sedimentation were recorded.
• Deposition characteristics in lower airway were estimated by matching results for St and γ.
• Orientations of deposited fibers were obtained by image processing method.
• Gravitational effect on the deposition cannot be neglected for 0.0228 < γ < 0.247.
Experiments carried out using a lung model with a single horizontal bifurcation under different steady inhalation conditions explored the orientation of depositing carbon fibers, and particle deposition fractions. The orientations of deposited fibers were obtained from micrographs. Specifically, the effects of the sedimentation parameter (γ), fiber length, and flow rate on orientations were analyzed. Our results indicate that gravitational effect on deposition cannot be neglected for 0.0228 < γ < 0.247. The absolute orientation angle of depositing fibers decreased linearly with increasing γ for values 0.0228 < γ < 0.15. Correspondence between Stokes numbers and γ suggests these characteristics can be used to estimate fiber deposition in the lower airways. Computer simulations with sphere-equivalent diameter models for the fibers explored deposition efficiency vs. Stokes number. Using the volume-equivalent diameter model, our experimental data for the horizontal bifurcation were replicated. Results for particle deposition using a lung model with a vertical bifurcation indicate that body position also affects deposition.