- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• TiO2 microspheres with flower-like morphology were synthesized through a w/o emulsion route.
• Microspheres before and after calcination had the same primary crystalline phase of anatase.
• The as-prepared microspheres had a higher photocatalytic activity than commercial TiO2 (P25).
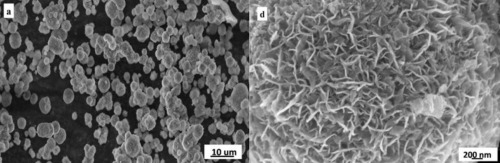
Mesoporous TiO2 microspheres with flower-like morphology, high specific surface area, and high-crystallinity primary crystalline-phase of anatase have been prepared through a water-in-oil emulsion synthesis route assisted by solvothermal treatment. The as-prepared powder microspheres, as well as their precursor, were characterized by various techniques. Thermogravimetry and differential thermal analysis indicated that the optimal sintering temperature of the TiO2 precursor was 550 °C. Field emission scanning electron microscopy, laser particle size analysis, and X-ray diffraction jointly confirmed that the precursor powder with a spherical structure and main particle sizes ranging from 3 to 20 μm had the same primary crystalline-phase as the TiO2 microspheres obtained from the calcination of the precursor at 550 °C for 4 h. The specific surface area of the TiO2 microspheres was approximately 123.6 m2/g according to the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) nitrogen adsorption results. Compared with the commercial TiO2 powder (P25), the resulting TiO2 microspheres exhibited a higher photocatalytic activity. Based on the experimental results, a rational mechanism was proposed to elucidate the formation of the TiO2 microspheres.