- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
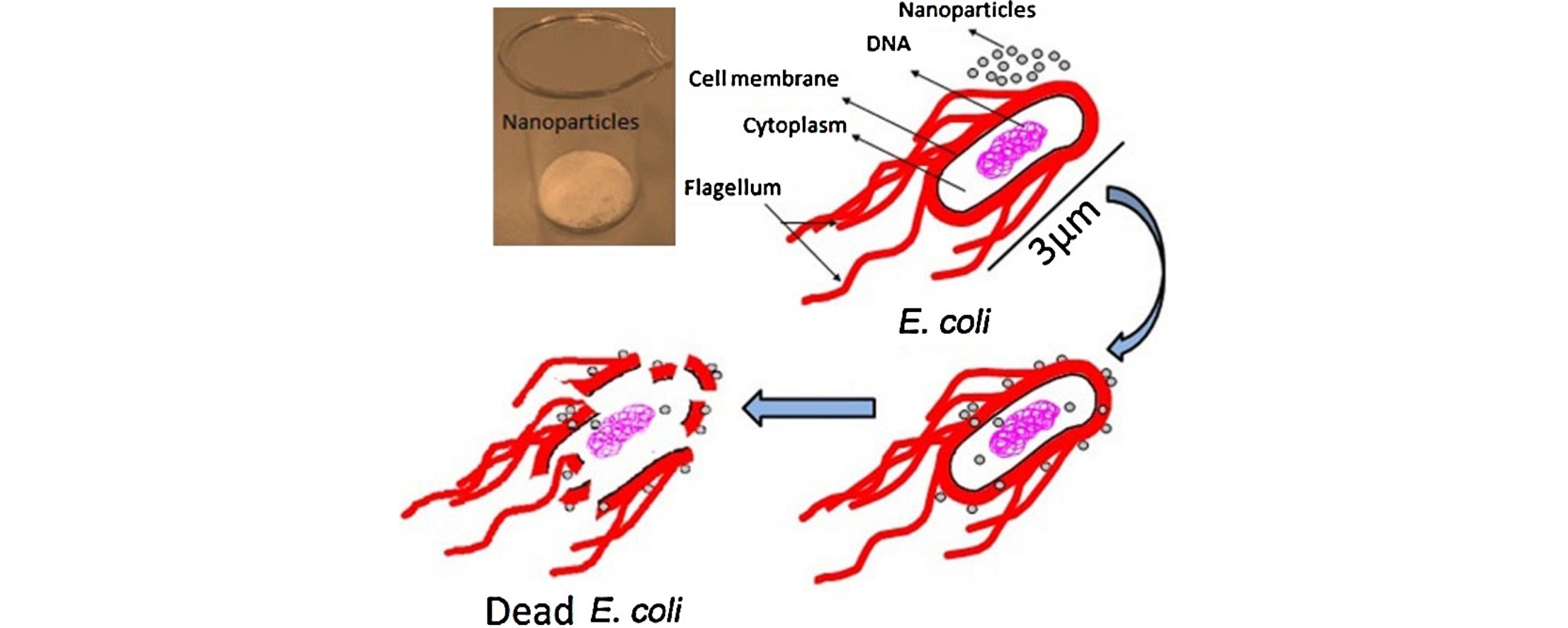
• CuxCo1−xFe2O4 nanoparticles (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) were synthesized by a co-precipitation method.
• Cu substitution caused decrease of particle size and crystallinity.
• Substitution of Co with Cu improved the antibacterial activity against E. coli.
Controlled growth and careful characterization of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for antibacterial applications are challenging. Copper-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles (CuxCo1−xFe2O4), where x = 0.0, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7 and 1.0, were synthesized using an economical and simple co-precipitation technique. The crystal structure and antibacterial properties of the samples as a function of Cu-substituted content were systematically studied. With increasing Cu concentration, the nanoparticle size decreased from ∼30 to ∼20 nm. The Fourier transform infra-red spectra exhibit two prominent fundamental absorption bands, at ∼595 and 419 cm−1. These bands correspond to intrinsic stretching vibrations of metals at tetrahedral and octahedral sites, respectively. The Raman scattering results reveal that increasing the Cu content enhances the local disorder at both tetrahedral and octahedral sub lattices. The results indicate that the substitution of Co with Cu in cobalt ferrite nanoparticles strongly influences the microstructure, crystal structure, and particle diameter, and also improves the antibacterial properties.