- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
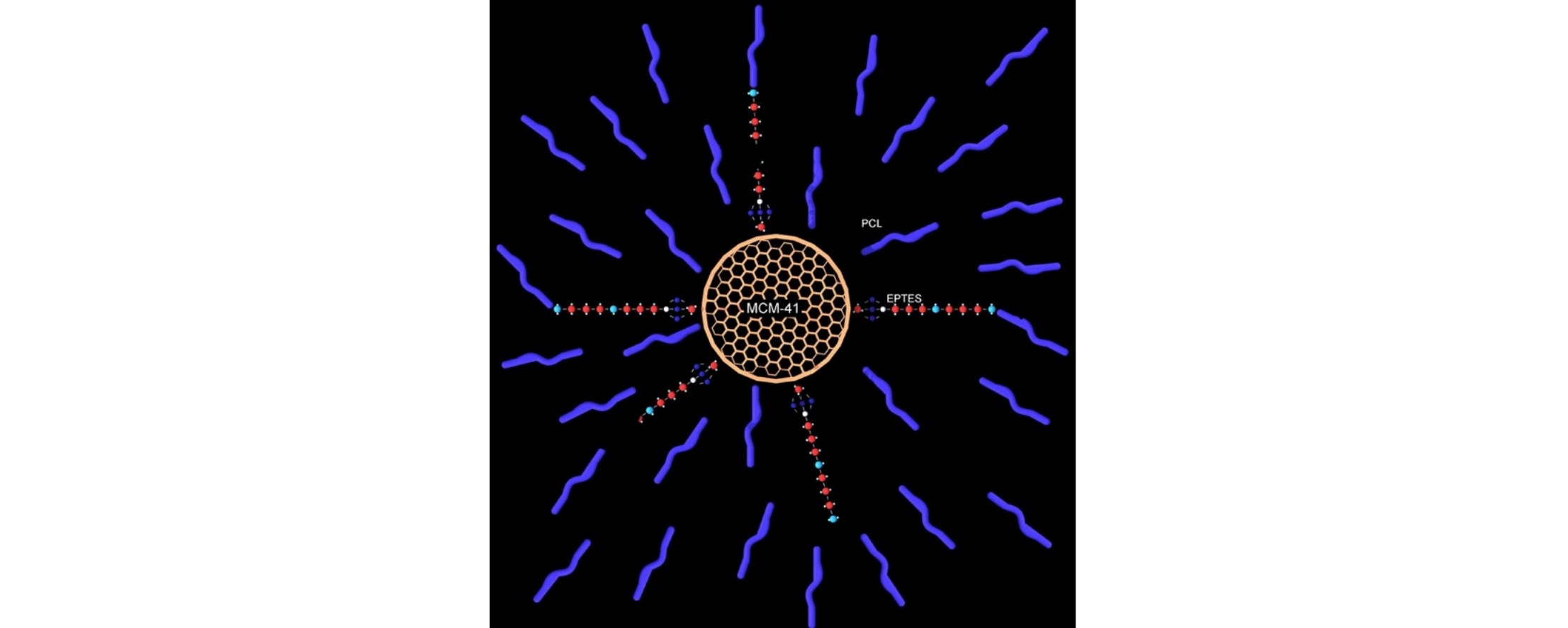
• Composites of PCL/MCM-41 and EPTES-functionalized MCM-41 were prepared by in situ polymerization.
• Different behaviour was observed for PCL composites prepared with MCM-41 and EPTES/MCM-41.
• EPTES/MCM-41 loadings of >2 wt% increased the temperature of maximum degradation rate by 55 °C.
• Improvement in PCL properties resulted from good interaction between filler and PCL matrix.
Composites of polycaprolactone (PCL) with mesoporous silica MCM-41 and N-[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]-ethylenediamine (EPTES)-functionalized MCM-41 (EPTES/MCM-41) were prepared by in situ polymerization. The thermal properties of the composites were characterized by thermogravimetric analysis. There was an increase in the thermal decomposition temperature of PCL by more than 55 °C, when the EPTES/MCM-41 loading was higher than 2 wt%. Tensile test results indicated that adding MCM-41 increased the brittleness of the PCL matrix, while adding 8 wt% of EPTES/MCM-41 increased the Young's modulus by 26%. Incorporating MCM-41 increased the crystallinity of the resulting PCL composite, compared with that of PCL. Incorporating up to 5 wt% EPTES/MCM-41 slightly reduced the crystallinity of PCL. The different effects of MCM-41 and EPTES/MCM-41 on the composite reflected the degree of interaction and dispersion of the silica filler in the polymer matrix, as evidenced by results from transmission electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy.
Nanocomposite; Mesoporous silica; Polycaprolactone
