- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
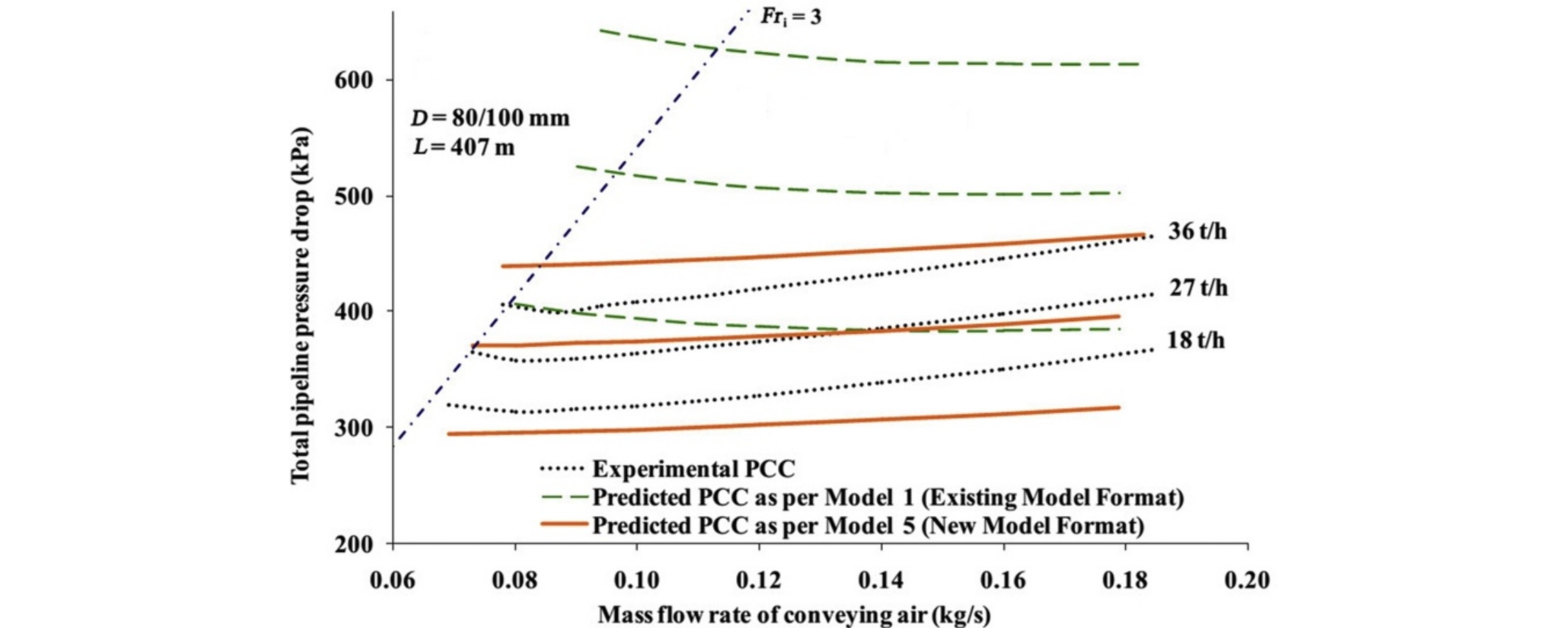
• A new model was developed in terms of volumetric loading ratio and dimensionless velocity.
• The model was evaluated for accuracy and stability for four solids, four pipelines.
• New model can provide reliable predictions when scaled-up compared with existing models.
Results are presented of an ongoing investigation into modeling friction in fluidized dense-phase pneumatic transport of bulk solids. Many popular modeling methods of the solids friction use the dimensionless solids loading ratio and Froude number. When evaluated under proper scale-up conditions of pipe diameter and length, many of these models have resulted in significant inaccuracy. A technique for modeling solids friction has been developed using a new combination of dimensionless numbers, volumetric loading ratio and the ratio of particle free settling velocity to superficial conveying air velocity, to replace the solids loading ratio and Froude number. The models developed using the new formalism were evaluated for accuracy and stability under significant scale-up conditions for four different products conveyed through four different test rigs (subject to diameter and length scale-up conditions). The new model considerably improves predictions compared with those obtained using the existing model, especially in the dense-phase region. Whereas the latter yields absolute average relative errors varying between 10% and 86%, the former yielded results with errors from 4% to 20% for a wide range of scale-up conditions. This represents a more reliable and narrower range of prediction that is suitable for industrial scale-up requirements.