- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
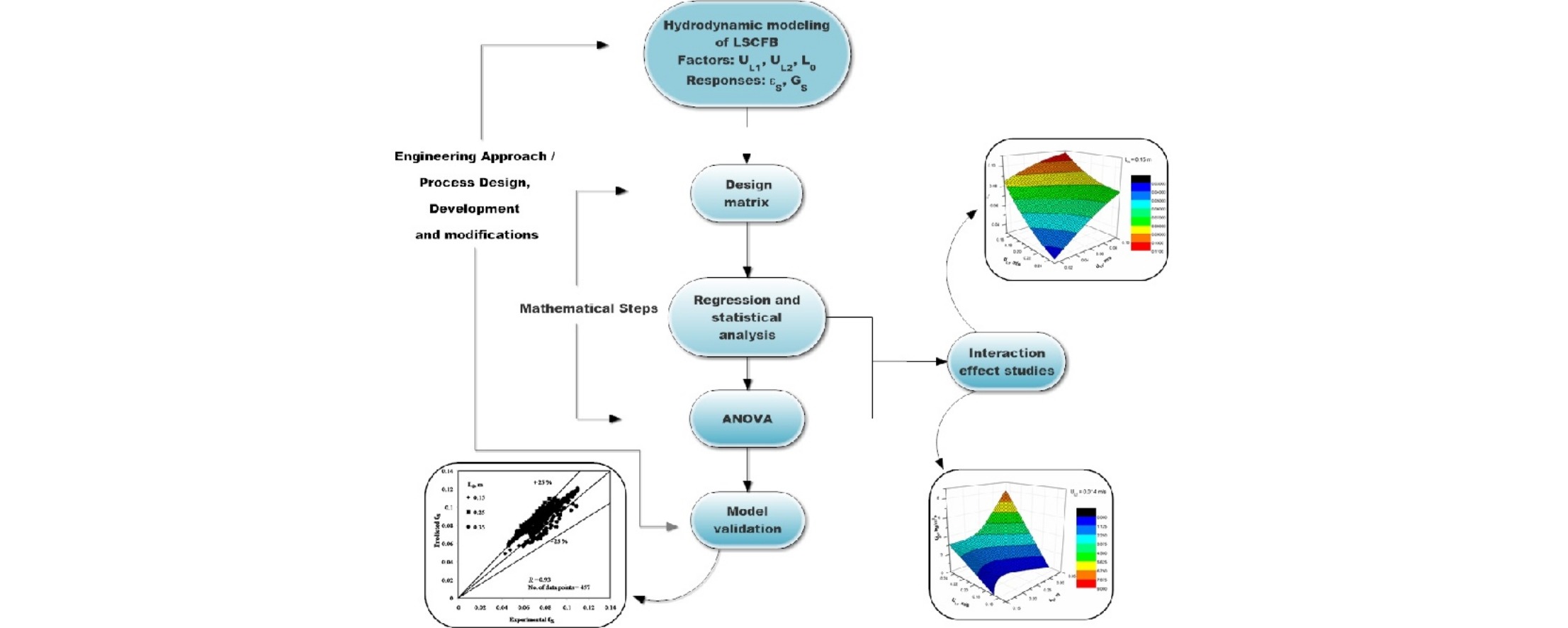
• Multilevel factorial design approach was used to model the liquid–solid circulating fluidized bed.
• Quadratic regression model was adopted to describe solids holdup and solids circulation rate.
• Validation of the model proved its reasonable adequacy.
• The developed model can be used to estimate the hydrodynamics of fluidization.
A design-of-experiments methodology is used to develop a statistical model for the prediction of the hydrodynamics of a liquid–solid circulating fluidized bed. To illustrate the multilevel factorial design approach, a step by step methodology is taken to study the effects of the interactions among the independent factors considered on the performance variables. A multilevel full factorial design with three levels of the two factors and five levels of the third factor has been studied. Various statistical models such as the linear, two-factor interaction, quadratic, and cubic models are tested. The model has been developed to predict responses, viz., average solids holdup and solids circulation rate. The validity of the developed regression model is verified using the analysis of variance. Furthermore, the model developed was compared with an experimental dataset to assess its adequacy and reliability. This detailed statistical design methodology for non-linear systems considered here provides a very important tool for design and optimization in a cost-effective approach.