- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
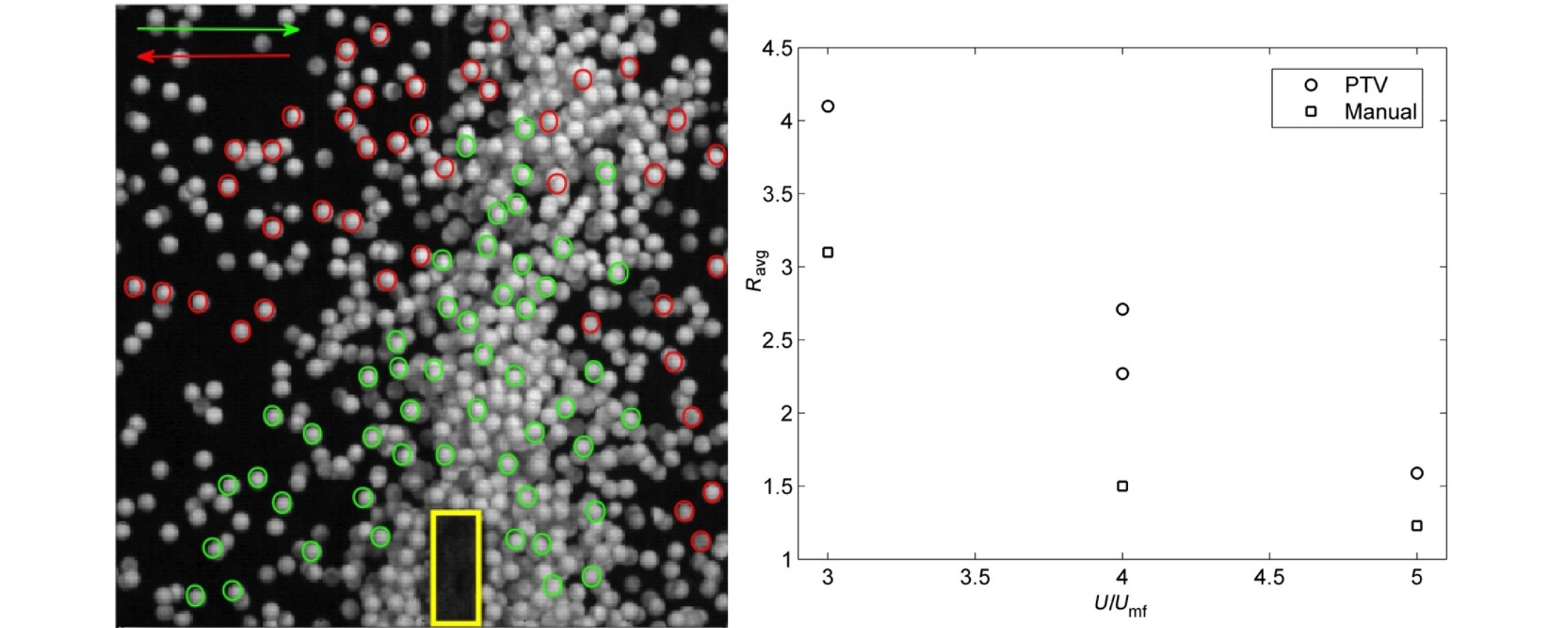
• Particle exchange rates at weirs in horizontal fluidised beds were studied.
• PTV-based methodology and a batch pseudo-2D fluidised bed were used.
• Particle exchange and internal circulation were investigated under various fluidisation conditions.
Residence time distributions (RTDs) in horizontal fluidised beds have a huge effect on solid product properties and are influenced by the internal design of the apparatus, e.g. the separation into different compartments by weirs. Weirs can be passed in or against the overall solid transport direction, with the back-flow resulting in axial dispersion, which is a measure of the spread of the RTD. Therefore, the ratio of exchange rates at weirs under different fluidisation conditions provides information on axial dispersion. In this work, a methodology based on particle tracking velocimetry is presented to obtain information on the exchange rates of particles at weirs in horizontal fluidised beds. The internal recirculation is studied for over-flow weirs with respect to different fluidisation conditions, providing a first step towards determining the effects of weirs and fluidisation conditions on axial dispersion and RTDs in horizontal fluidised beds.