- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
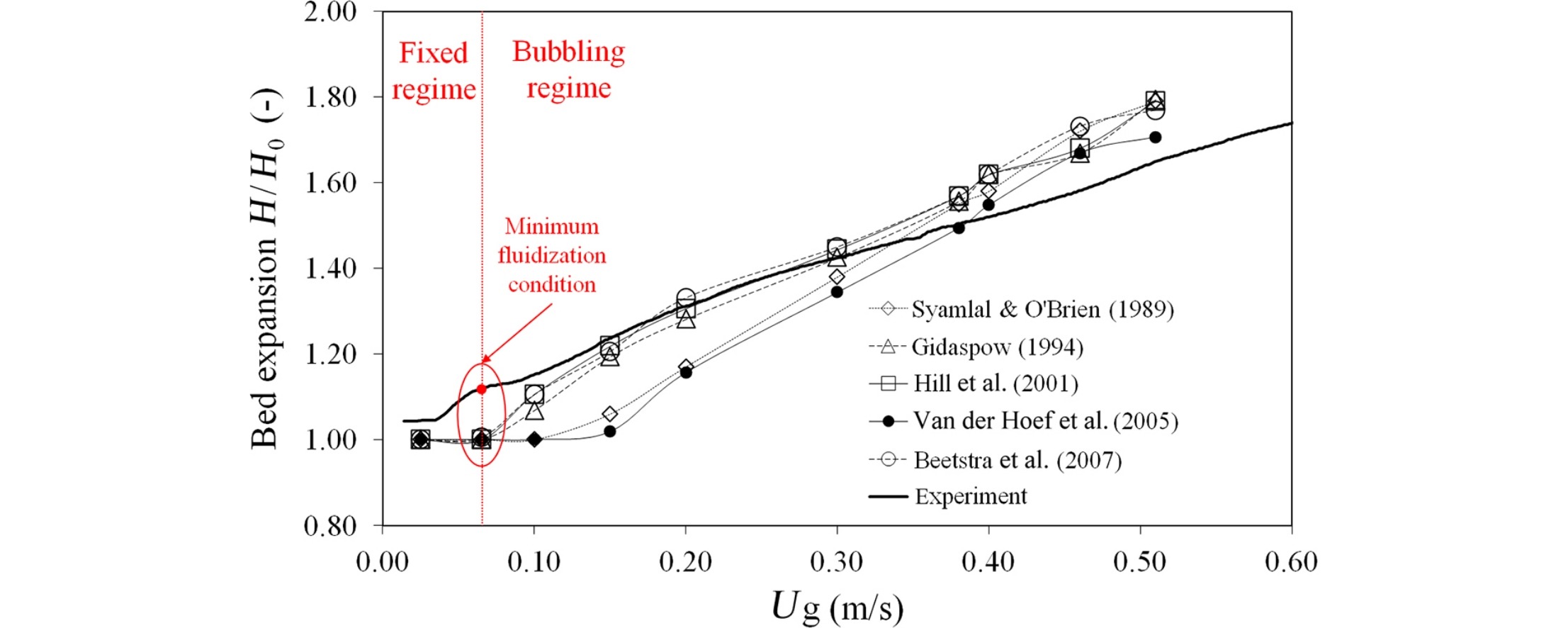
• Empirical and LBM-based drag models were compared and evaluated with experiments.
• Bubbling fluidized bed simulations using LBM-based drag models were realized.
• LBM based drag models can predict the design parameters of a fluidized bed fairly well.
In simulations of fluidized beds using computational fluid dynamics (CFD), the description of gas–solid flow hydrodynamics relies on a drag model to account for the momentum transfer between gas and solid phases. Although several studies of drag models have been published, there have been few investigations of the application of lattice Boltzmann method (LBM)-based drag models to bubbling fluidized bed simulations. In the present study, a comprehensive comparison of empirical and LBM-based drag models was carried out to assess the performance of these models during simulations of gas–solid flow hydrodynamics in a bubbling fluidized bed. A CFD model using the MFIX code based on the Eulerian–Eulerian approach and the kinetic theory of granular flow was used to simulate a 2D bubbling fluidized bed with Geldart B particles. The simulation results were validated by comparison with experimental data. Statistical analysis of the results shows that LBM-based drag models can reliably model gas–solid flow hydrodynamics in a bubbling fluidized bed.