- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Extinction characteristics of three biofuel production microalgae were measured.
• An improved transmission method for measuring extinction coefficient was presented.
• Optical constants of the cultivation media of microalgae were measured.
• Extinction efficiency of the microalgae cells was presented and compared.
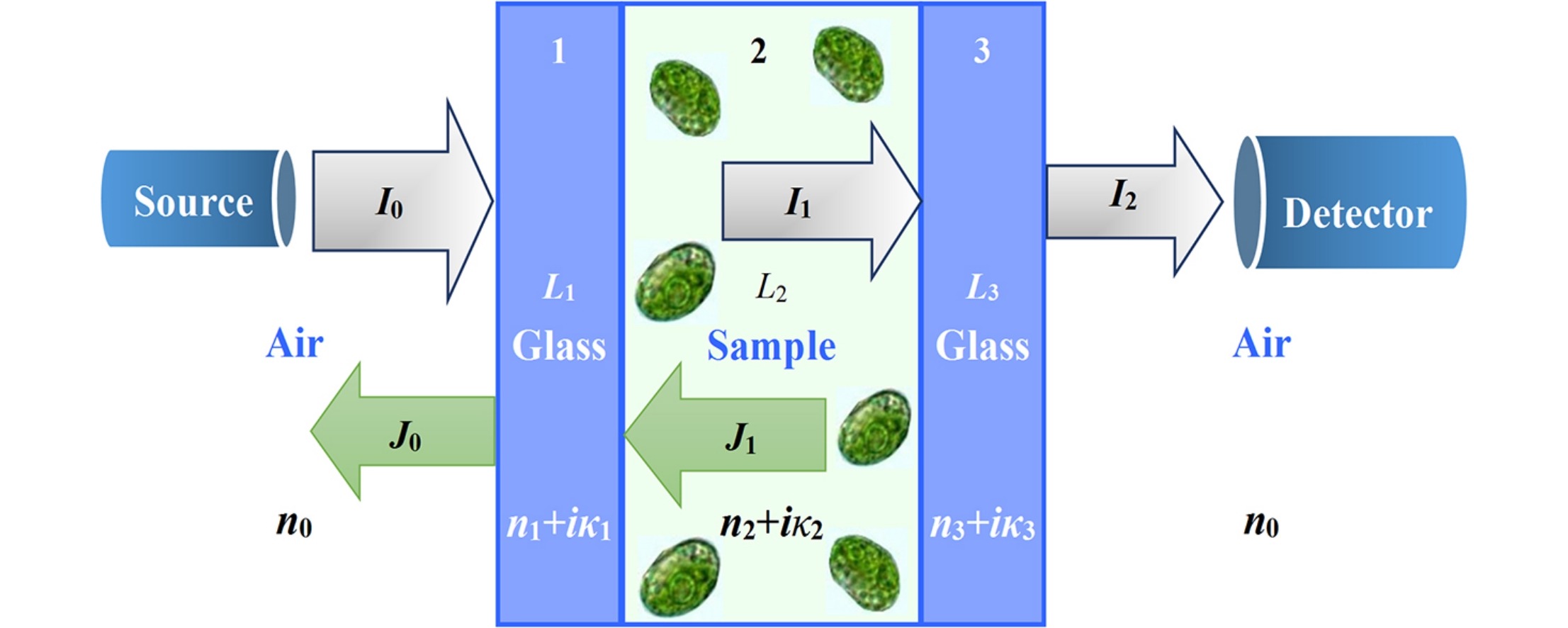
The optical extinction characteristics of the three kinds of microalgae Nannochloropsis maritima, Ellipsoidion sp. (277.03), and Dunaliella tertiolecta were determined using an improved transmission method, in the 300–1800 nm spectral range. These three microalgae are promising candidates for the production of biofuels such as bio-hydrogen and biodiesel. The improved transmission method determines the spectral extinction coefficient of the microalgae. This is based on the measured transmittance, and employs an optical model that takes into consideration multiple reflections and refractions at the air–glass and glass–liquid interfaces. Silicon dioxide microspheres of monodisperse size were used as a model to verify the proposed method. The optical constants of the culture medium, size distributions, and extinction cross-sections of the microalgae cells were measured and analyzed. The improved transmission method is demonstrated to yield more accurate results than the traditional method. The spectral extinction efficiencies of the three kinds of microalgae show significant differences in the near ultraviolet and visible spectral regions. The spectral extinction efficiencies also exhibit small differences in the longer wavelength range of 950–1800 nm, with values generally less than 1.0. The measured extinction characteristics data of the three microalgae and the presented measurement method will facilitate process modeling in photobioreactors for biofuel production.