- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
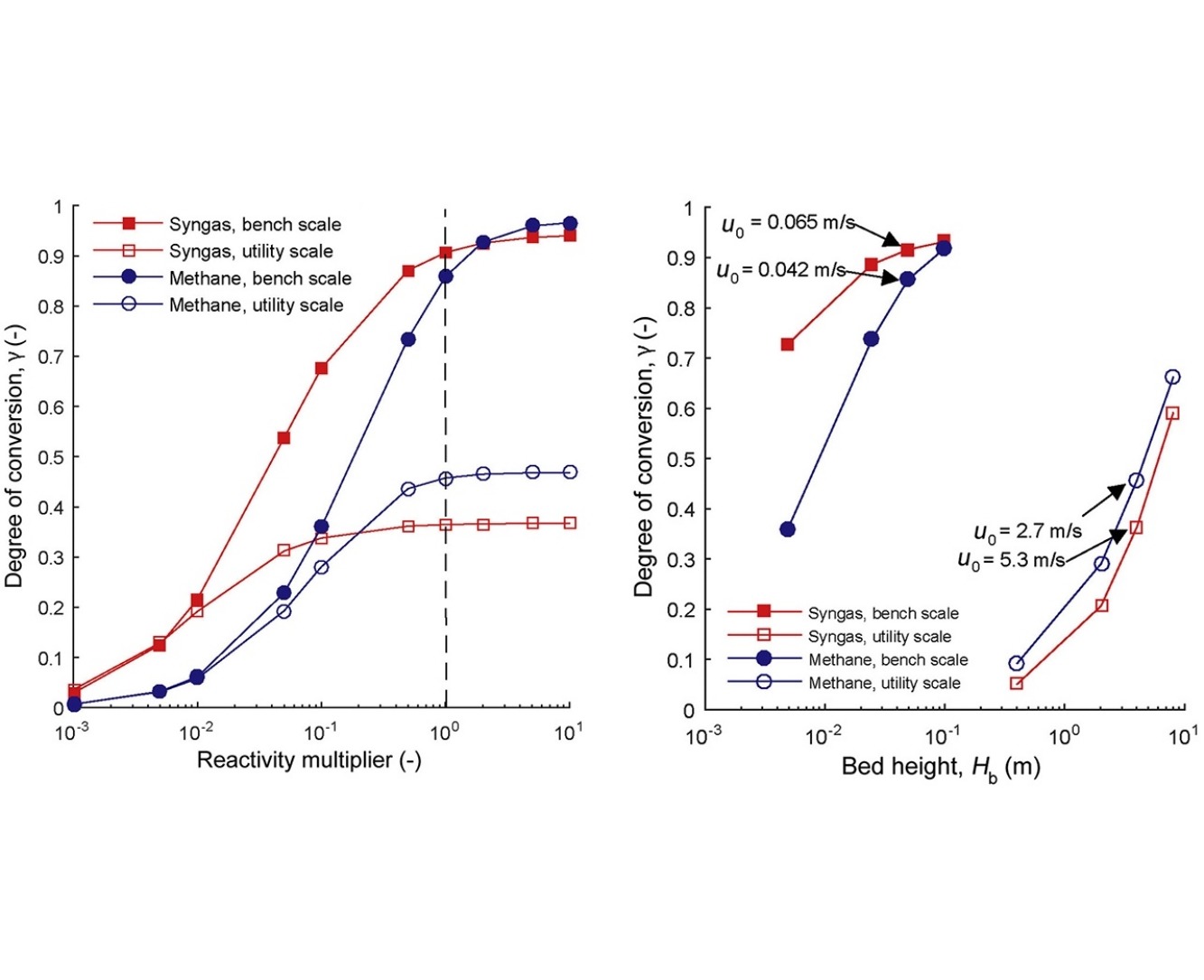
• Gas conversion in the bottom bed of a chemical looping combustion fuel reactor was studied.
• A semi-empirical model was constructed and then verified against experiments.
• The effects of scale-up to utility scale were studied.
• Mass transfer between bubble and emulsion phase limited fuel conversion at utility scale units.
This work investigates the scale-up of chemical looping combustion (CLC), a next-generation technology for carbon capture and storage, to the industrial scale. The study focused on the bottom bed of the unit, which was considered to be the critical region during scale-up due to the large solids inventory in this zone combined with relatively inefficient gas–solids contact. Two CLC reactors of vastly different sizes (bench and utility scale) were studied to discern their difference related to scale-up via a one-dimensional model. This model considered kinetics that varied with the degree of oxidation and population distribution of the oxygen carriers, the mixing of which accounts for both convective and dispersive transport. The model was validated against bench scale data, and was used to evaluate the performance of a 1000 MWth CLC fuel reactor using either syngas or methane as fuels. Sensitivity analyses were also carried out with this model to determine the effects of several parameters on fuel conversion, including solids circulation, oxygen carrier reactivity, bed height, and maximum bubble size. The results show that the mass transfer of gas from bubbles to the emulsion phase represents a significant limiting factor for fuel conversion in the bottom bed of a utility scale fuel reactor.