- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
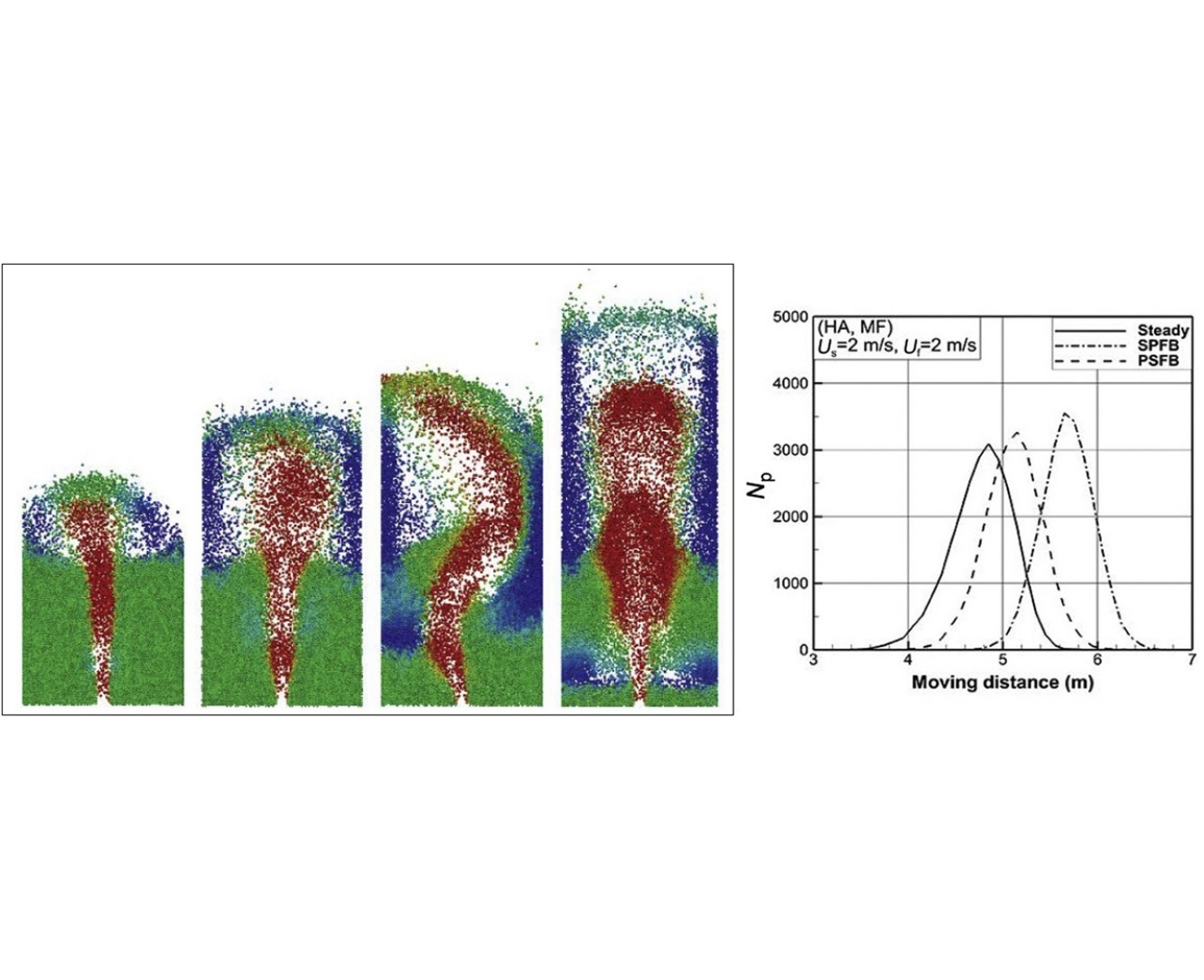
• Effect of flow pulsations on a spout-fluid bed was investigated.
• Pressure drop was shown to be a function of pulsation parameters and configuration.
• Pulsation enhanced particle motion and bed behavior with equal air consumption.
• Up to 19% increase in average moving distance showed applicability of pulsation.
Effects of variable airflow on particle motion in spout-fluid beds are studied. Computational fluid dynamics using Navier–Stokes equations for the gas phase coupled with the discrete element method using Newton's laws for the solid phase have been employed. Results indicate that increasing the fluidizing velocity diminishes dead zones and increases both the total height of the bed and the traversed distance by particles in the steady spout-fluid bed. In pulsed airflows, two configurations are investigated, namely, the spouted pulsed-fluidized bed with pulsed flow of the fluidizing velocity, and the pulsed-spouted fluidized bed with pulsed flow of the spouting velocity. The positive effect of pulsation on particle motion is shown and the effects of parameters, such as amplitude and frequency, on the dynamics of the bed are investigated in each configuration. An increase of up to 19% in traversed distance is found for the range studied, which suggests flow pulsation as a promising technique for increasing particle mixing in spout-fluid beds.