- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
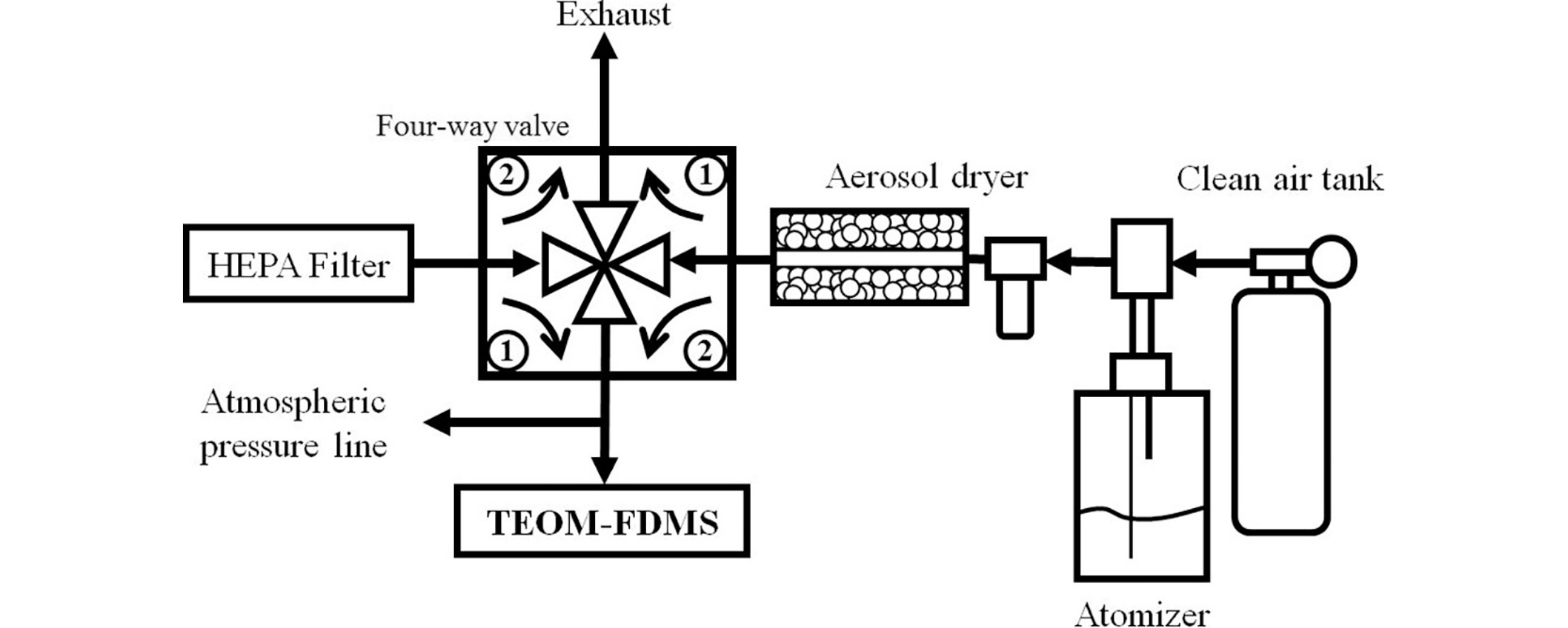
• TEOM instruments currently used pre-weighted filters as calibration weight.
• Calibration weights are not representative of atmospheric particle mass measurements.
• Calibration weights overlook technical problems in sampling and microbalance filtration systems.
• It is necessary to establish a PM standard for such particle mass concentration instruments.
The tapered element oscillating microbalance with filter dynamics measurement system (TEOM-FDMS) is an instrument commonly employed by the French air quality monitoring network. This instrument is currently calibrated with calibration weights traceable to SI but having value and mass differences between each of them that are not representative of real atmospheric particle mass measurements. Moreover, these calibration weights do not allow detection of any technical problems associated with either the TEOM-FDMS sampling system upstream of the mass measurement or the intrinsic TEOM-FDMS filtration system. Therefore, a calibration method was developed using a portable reference aerosol generator (PRAG) that produces known and stable particle mass concentrations over time. Here, we present the characterization of the PRAG system in terms of a reference range of particle masses between 30 ± 10 and 3456 ± 83 μg at three sampling times. Its coupling with the TEOM-FDMS and a global comparison between the defined reference range of particle masses and the measured masses obtained with each TEOM-FDMS implicated in this study are also presented.