- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
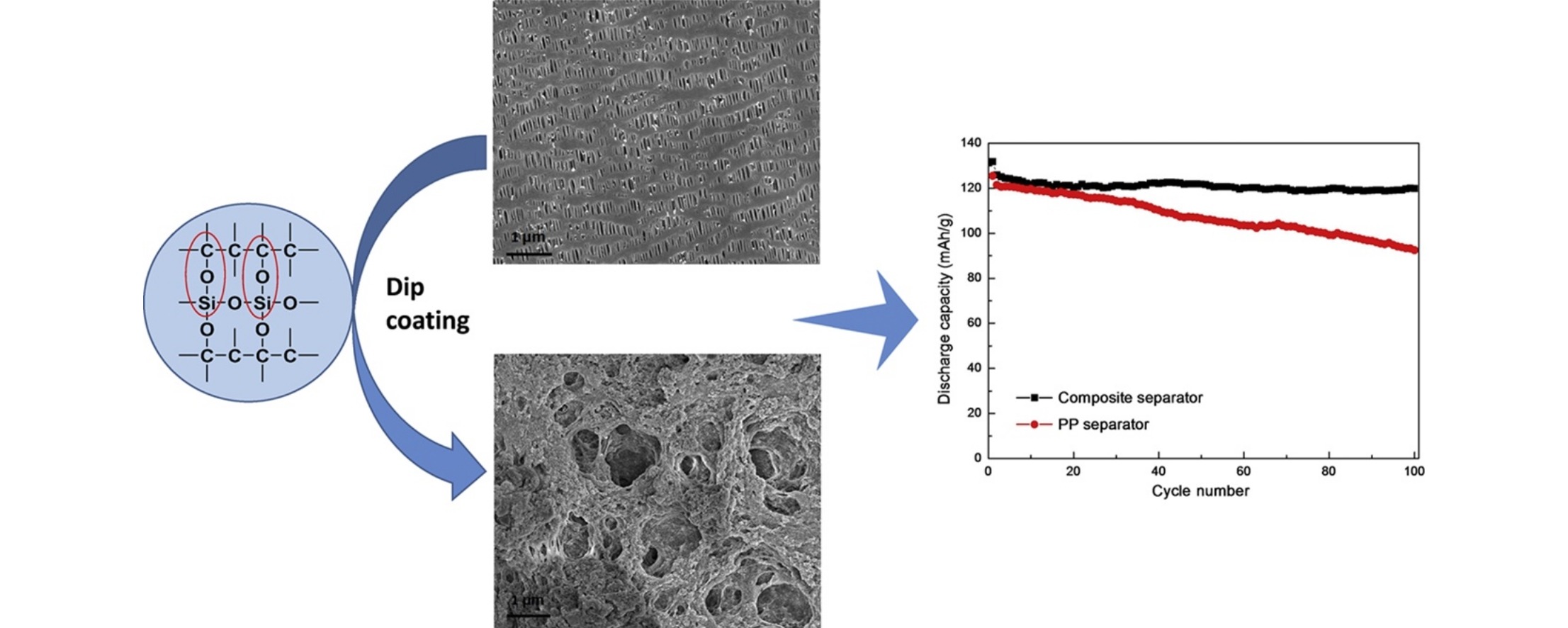
• Nano-SiO2/PVA-coated PP composite separators were fabricated by sol–gel and dip-coating methods.
• Effects of the tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) dosage on the composite separators were investigated.
• Composite separator using 7.5 wt% TEOS exhibited better electrochemical performance.
To improve the electrolyte wettability and thermal stability of polypropylene (PP) separators, nano-SiO2/poly(vinyl alcohol)-coated PP composite separators were prepared using a simple but efficient sol–gel and dip-coating method. The effects of the tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) dosage on the morphology, wettability, and thermal stability of the composite separators were investigated using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and contact-angle measurements. All the composite separators gave a smaller contact angle, higher electrolyte uptake, and lower thermal shrinkage compared with the PP separator, indicating enhanced wettability and thermal stability. Unlike the case for a traditional physical mixture, Si—O—C covalent bonds were formed in the coating layer. The composite separator with a TEOS dosage of 7.5 wt% had a unique porous structure combining hierarchical pores with interstitial voids, and gave the best wettability and thermal stability. The ionic conductivity of the composite separator containing 7.5 wt% TEOS was 1.26 mS/cm, which is much higher than that of the PP separator (0.74 mS/cm). The C-rate and cycling performances of batteries assembled with the composite separator containing 7.5 wt% TEOS were better than those of batteries containing PP separators.