- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
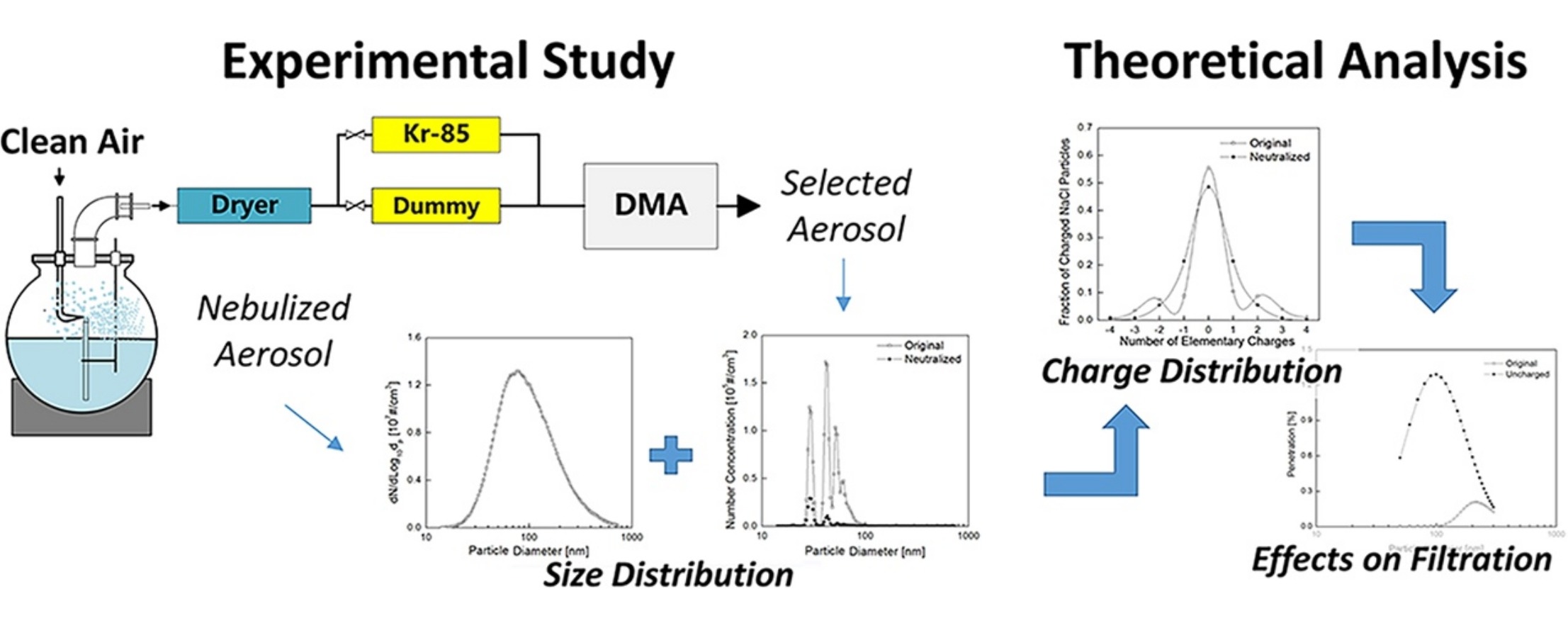
• Charge state of particles generated by nebulization was studied.
• NaCl aerosol was overall positively charged with a mixture of neutral and charged particles.
• Diethylhexyl sebacate aerosol was found to be electrically neutral.
• Charges on nebulized NaCl aerosol enhanced the filtration efficiency of HEPA filters.
There have been few investigations of effects of electrical charge, carried by lab-generated particles, on filtration efficiency testing. Here, we measured the elementary charge on particles and the fraction of particles carrying that charge with a combined electrometer, differential mobility analyzer, and scanning mobility particle sizer. A typical solid NaCl aerosol and liquid diethylhexyl sebacate (DEHS) aerosol were generated with Collison and Laskin nebulizers, respectively. Our experimental results showed that NaCl aerosols carried more charge after aerosol generation. The average net elementary charge per particle was approximately 0.07. The NaCl aerosol was overall positively charged but contained a mixture of neutral and charged particles. Individual particles could carry at most four elementary charges. According to constant theorem, we speculated that original NaCl aerosol contained 17% neutral, 45% positive-, and 38% negative-charged particles in the diameter range from 30 to 300 nm. A Kr-85 neutralizer was used to decrease the charge on the NaCl particles. Our results indicated that the DEHS aerosol was electrically neutral. The effects of electric charge on particle collection by electret and electroneutral high efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters were analyzed. Theoretical calculations suggested that charges on original NaCl aerosol particles enhanced the filtration efficiency of HEPA filters.