- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• The Al2O3 and SiO2 nanoparticles used were spherical and mildly aggregated in engine oil.
• Viscosity of nanolubricants increased with volume fractions of nanoparticles added.
• Nanoparticles at lower volume fractions were more effective in terms of wear and engine performance.
• Nanolubricant with 0.3 vol% Al2O3 nanoparticles exhibited best tribological and engine performance.
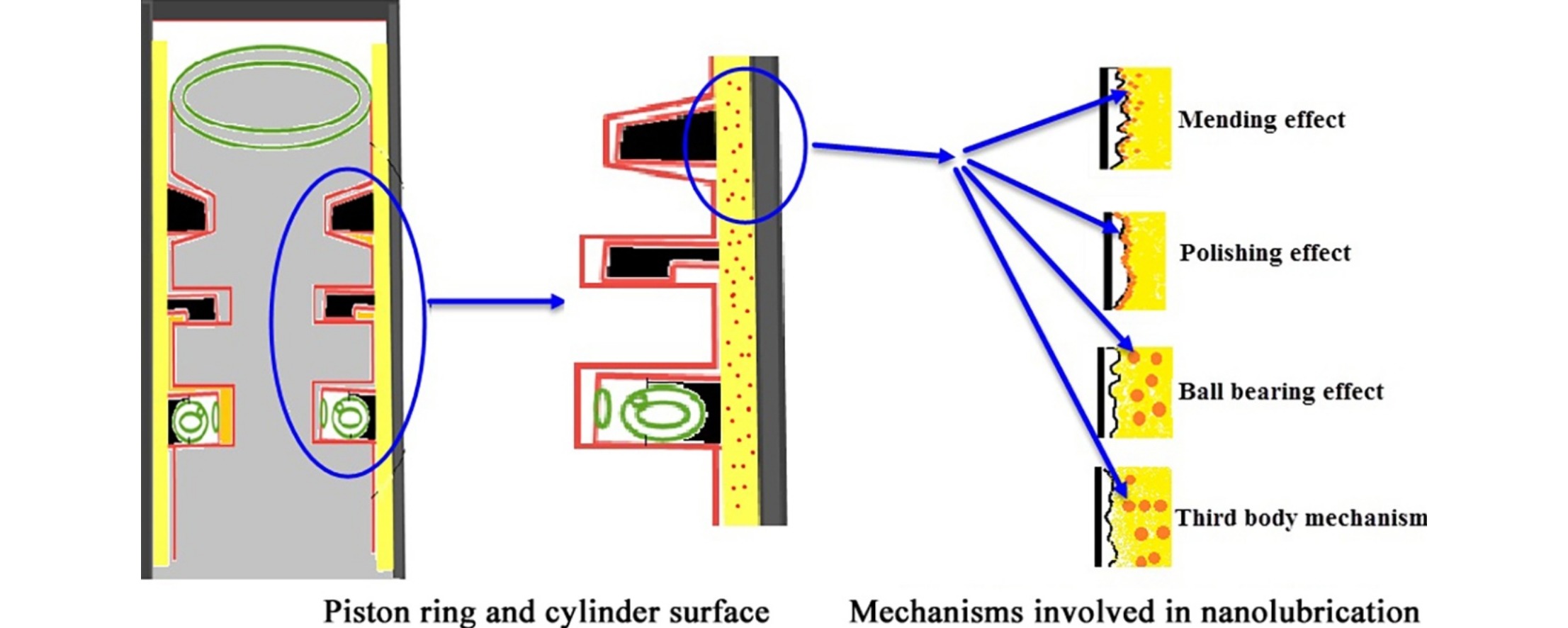
In the present study, the performance of a 4-stroke diesel engine was experimentally evaluated upon adding Al2O3 or SiO2 nanoparticles to the engine oil (SAE15W40). The viscosity and density of the resulting nanolubricants were determined while varying both the nanoparticle volume fraction and the temperature. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE–SEM) showed that the nanoparticles had a spherical morphology and dynamic light scattering analysis determined some aggregation of the nanoparticles in the engine oil. A pin-on-disc test apparatus was used for friction and wear analysis in the presence of the nanolubricants. Examination of wear scars by FE–SEM and energy dispersive spectroscopy found evidence of ball bearing and surface polishing effects, which were responsible for improvements in the tribological properties of the oil. The performance of these nanolubricants in a 4-stroke diesel engine test rig was assessed, and the greatest improvements in the tribological behavior and engine performance were observed when employing 0.3 vol% Al2O3.