- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
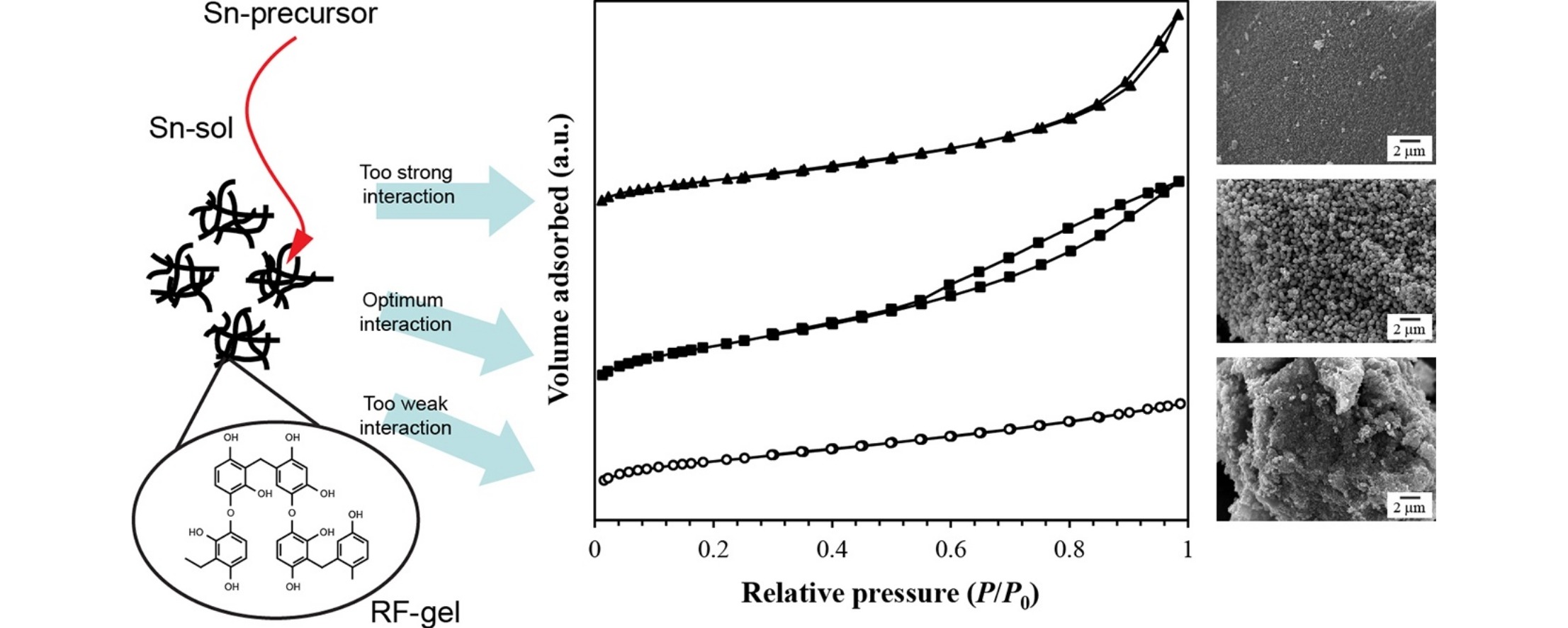
• Resorcinol–formaldehyde (RF) gel was used a template to synthesize mesoporous tin dioxide.
• Surface area and mesoporosity of the products could be controlled by the synthesis parameters.
• Interactions between RF network and tin-containing sol were the key factor affecting mesoporosity.
Tin dioxide is a useful n-type oxide semiconductor used in a variety of applications owing to its superior optical, electrical, and multifunctional properties. Here, we used a network of resorcinol–formaldehyde (RF) gel to synthesize mesoporous tin dioxide via a sol–gel process. The effects of various synthesis parameters on the morphology and mesoporosity of the obtained product were investigated, including aging time of the RF gel, tin-to-formaldehyde molar ratio, resorcinol-to-carbonate molar ratio, and the aging time of the tin/RF mixed gel. Our experimental results showed that the interaction between the network of the RF gel and tin-containing sol is a key factor that affected the structural strength of the porous network and the porosity of the final product. Through control of the interactions in the tin/RF mixed gel we obtained porous tin dioxide materials that could be effectively used to form large-surface area films with desirable mesoporous properties.