- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
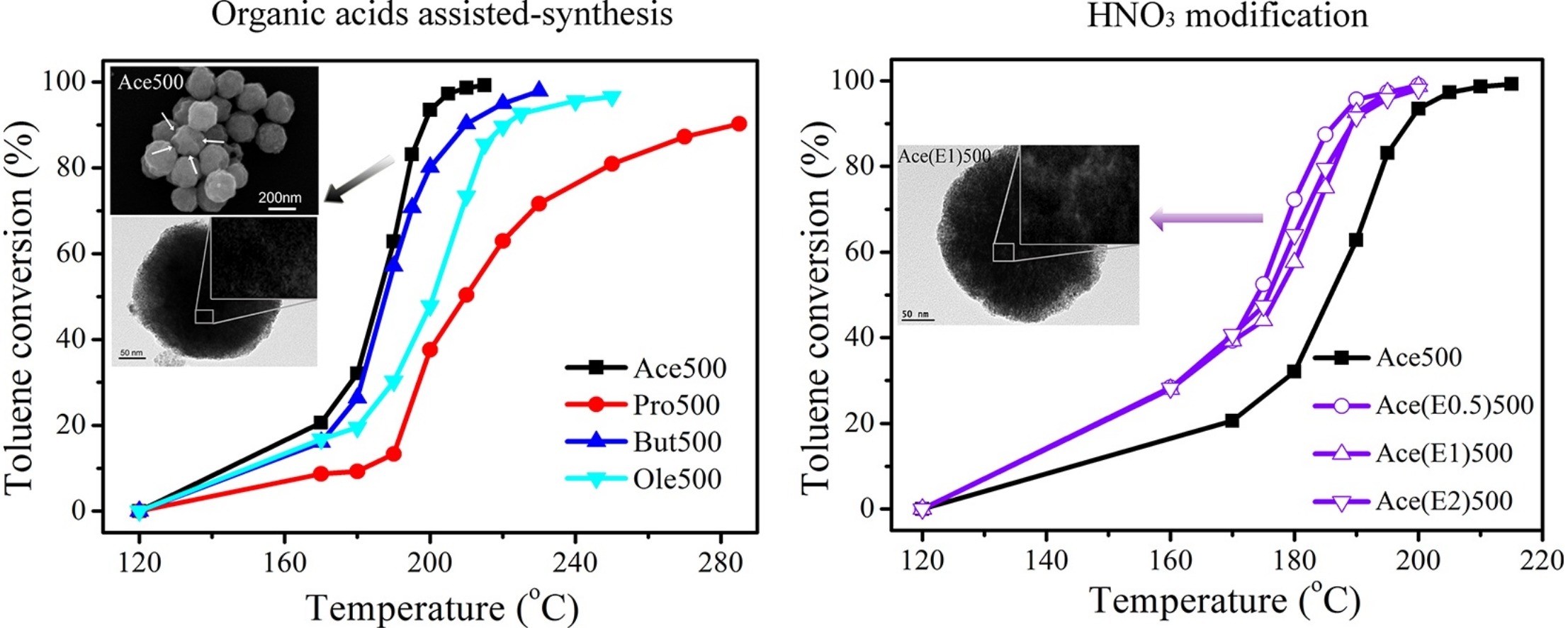
• Microstructured CeO2 were prepared via a solvothermal method assisted with various organic acids.
• CeO2 synthesized with acetic acid showed a better performance for toluene catalytic combustion.
• The activity can be attributed to its hierarchical porosity and surface-active oxygen content.
CeO2 is an important porous material with a wide range of applications in the abatement of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). In this paper, we prepared a series of novel three-dimensional (3D) micro/nanostructured CeO2 materials via a solvothermal method. Organic acid-assisted synthesis and inorganic acid post-treatment were used to adjust the CeO2 microstructures. The size of the 3D micro/nanostructures could be controlled in the range from 180 nm to 1.5 μm and the surface morphology changed from rough to smooth with the use of different organic acids. The CeO2 synthesized with acetic acid featured a hierarchical porosity and showed good performance for toluene catalytic combustion: a T50 of 187 °C and a T90 of 195 °C. Moreover, the crystallite size, textural properties, and surface chemical states could be tuned by inorganic acid modification. After treatment with HNO3, the modified CeO2 materials exhibited improved catalytic activity, with a T50 of ∼175 °C and a T90 of ∼187 °C. We concluded that the toluene combustion activity is related to the porosity and the amount of surface active oxygen of the CeO2. Both these features can be tuned by the co-work of organic and inorganic acids.