- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
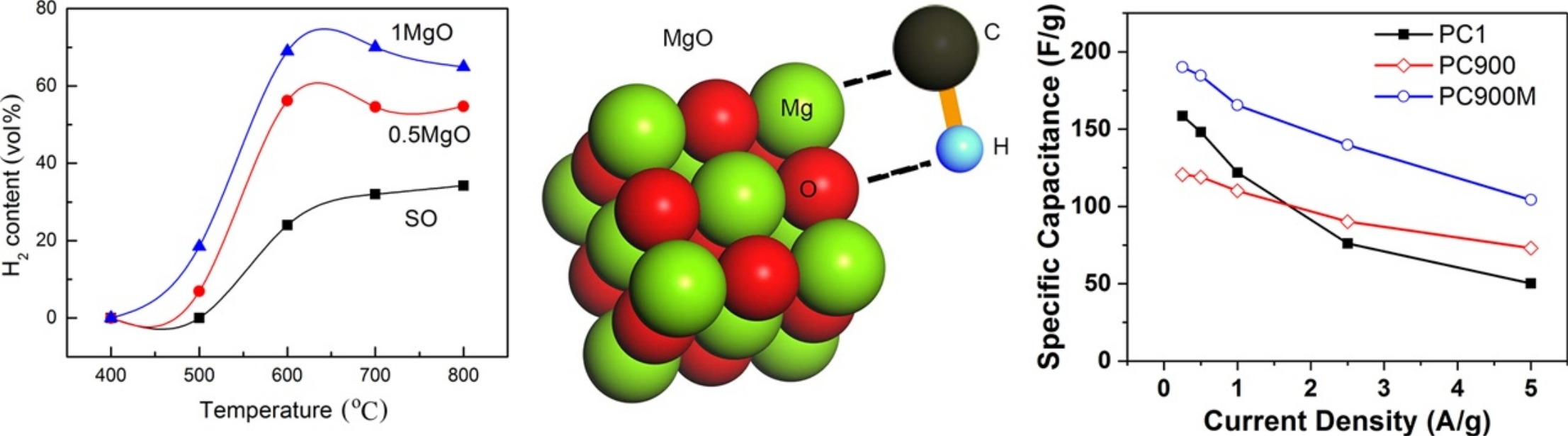
• Carbonization and 900 °C heat treatment of slurry oil/MgO composites were investigated.
• Results showed that MgO promoted the breakage of C—H bonds during the carbonization.
• Heat treatment of carbonized composites enhanced the electrode performance of the porous carbon.
Although MgO has been widely used for the MgO-templated synthesis of carbon materials, little attention has been paid to MgO's catalytic function during carbon deposition. Here, a systematic analysis of the products of slurry oil (SO) carbonization with and without MgO templates present indicates that MgO catalytically promoted the breakage of C—H bonds by immobilizing heavy oil molecules on MgO surfaces and the attractive interaction between hydrogen and MgO. Compared with the carbonization of SO alone, a notably higher H2 concentration and a lower hydrocarbon concentration was observed in the tail gas, a higher solid yield and a lower degree of graphitization of the carbon product were observed when MgO was also present. Furthermore, treatment at 900 °C in the presence of MgO efficiently enhanced the capacitance and rate capability of the as-obtained porous carbon when tested as an electrode material for supercapacitors. These results suggest that the catalytic function of MgO could exist in all MgO-templated syntheses and in the heat treatment of porous carbons and graphene.