- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
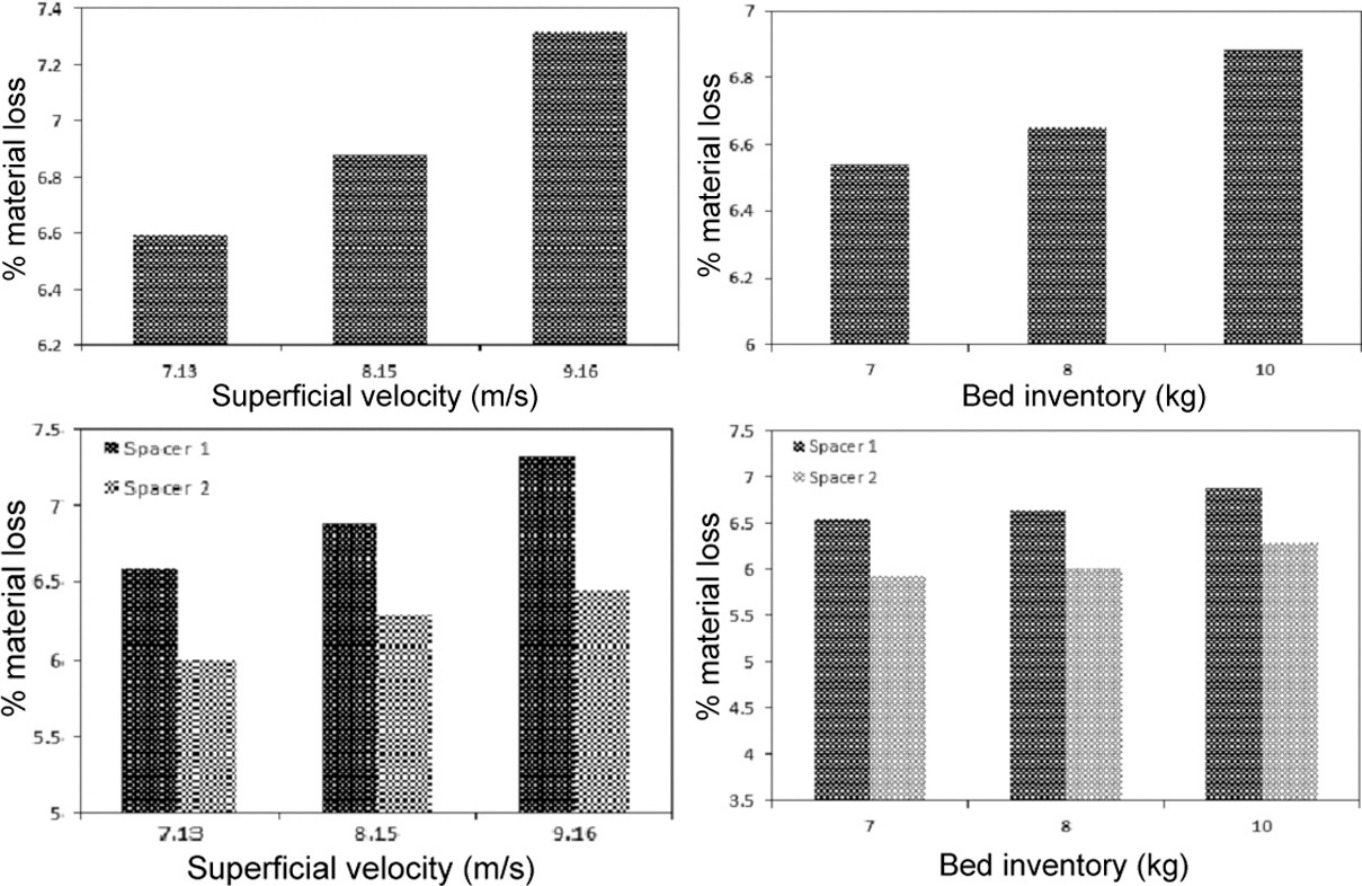
• Effects of various parameters on the attrition of bed particles were studied in a RCFB.
• Attrition of sand particles was found to be significantly affected by operation time.
• Particles of size less than 300 μm were found to be elutriated with fluidizing air.
• Material loss was significant with higher superficial velocity, bed inventory and spacer height.
We performed an experimental study to investigate the effects of various parameters on the attrition of bed material and its size distribution with increasing operation time in a recirculating fluidized bed (RCFB). The studied parameters included superficial velocity of fluidizing air, bed inventory, and spacing between the jet top and draft tube bottom (spacer height). The bed material was prepared from Indian Standard (IS) Grade I sand from sieves with a size range of 2.20–1.00 mm. Experiments were performed at ambient conditions, with the superficial air velocity ranging from 7.13–9.16 m/s, a bed inventory of 7–10 kg, spacing of 0.085 and 0.045 m between the jet top and draft tube bottom, and an operating time of 40 h. We investigated the influence of these parameters in terms of changes in the size distribution of particles, changes in the %-weight of particles of different size ranges, generation of particles with smaller diameters, the decrease of the downcomer bed height, variations in the coefficient of uniformity and coefficient of curvature, and material loss from entrainment of fines with increasing operation time. The mode of attrition was abrasion in all experiments. We found that with increasing operation time and other parameters (bed inventory, superficial air velocity, and spacer height) attrition of the bed material also increased. Generation and elutriation of fines were more pronounced at higher superficial air velocity, bed inventory, and spacer height.