- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
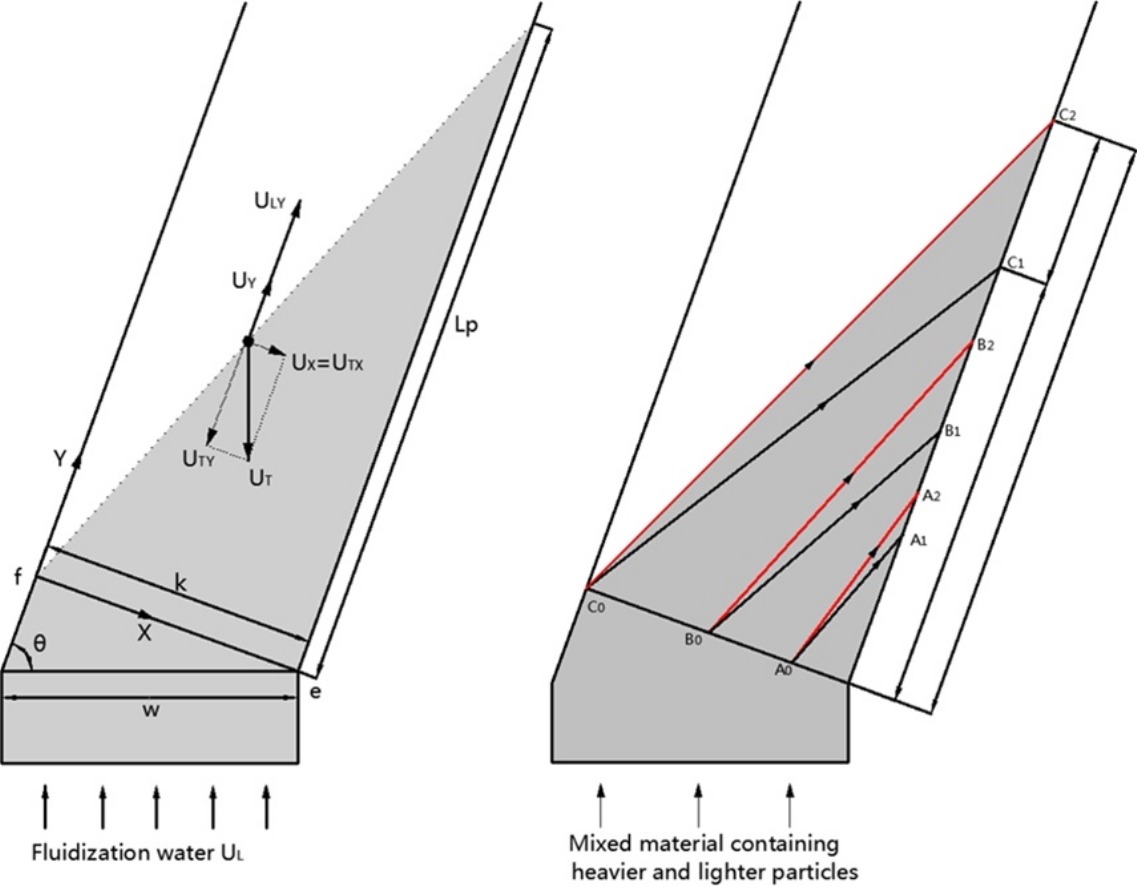
• A model of binary particle settling in modified fluidised bed with inclined channel was proposed.
• The model predicted particle settling lengths were in reasonable agreement with experimental data.
• The bed utilization factor and separation efficiency decreased with increasing the water velocity.
Rectangular inclined channels prove promising for solid classification based on the principle of particle differential sedimentation. In the present work, we investigated the motion characteristics of binary solids in a modified fluidised bed (mFB) with inclined plates. We developed a theoretical model for the particle motion behaviour that accounts for the average solid volume fraction in the inclined channel and interactions between binary solids. The experimental system was designed to be consistent with the idealised theoretical arrangements to maximise the measurement accuracy. The experimental particles were mixtures of silica sand particles of sizes 425–710 μm and 710–880 μm, respectively. Specifically, we investigated the flow hydrodynamics of the binary suspension in terms of the settling length of both particle species and the bed expansion behaviour. We also analysed the utilisation factor and the separation efficiency of the mFB. The results showed that the average solid volume fraction in the inclined channel fluctuated slightly for a given total solid inventory. The utilisation factor and separation efficiency of the system decreased when increasing either the fluidisation velocity or the solid inventory. The prediction results were in good agreement with the experimental data with an absolute deviation of less than 15%.