- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
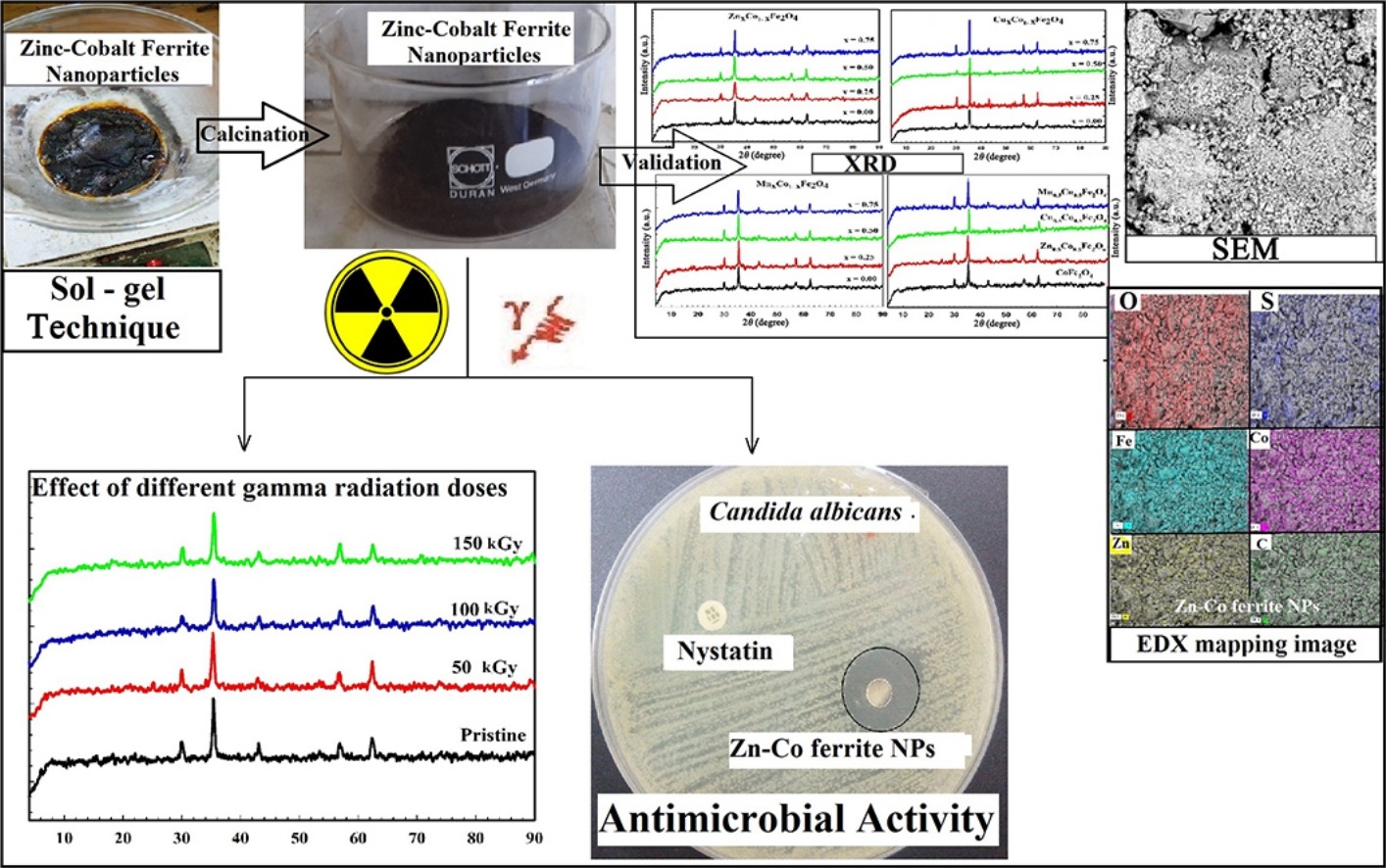
• Zn, Cu, and Mn substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles were synthesized by sol–gel method.
• Antimicrobial activity of the ferrites against selected pathogens was studied.
• Of the prepared ferrites, zinc cobalt ferrite (ZCFO) possessed strongest antimicrobial activity.
• Irradiation at 150 kGy decreased ZCFO particle size and elevated its antimicrobial potential.
Metal-substituted cobalt ferrites [MxCo(1−x)Fe2O4 (M = Zn, Cu, Mn; x = 0.0, 0.25, 0.5, and 0.75)] were synthesized via a sol–gel technique. The ferrite structures were confirmed by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, surface analysis using the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller method, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Antimicrobial activity of these ferrites against selected pathogenic microbes was determined. The structures remained cubic spinel phases after substitution of metals. Substitution strongly influenced the microstructure and homogeneous grain distribution. The particle size of the ferrites increased linearly with increase in their annealing temperature. The surface area of zinc cobalt ferrite nanoparticles (ZCFO) was 52.56 m2/g, the average pore size was 1.84 nm, and pore volume was 0.136 mL/g. All ferrites showed antimicrobial activity toward all pathogens selected. Of these, the most powerful was ZCFO, showing zones of inhibition of 13.0 mm against Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus and 12.0 mm against Candida albicans. Gamma-irradiated ZCFO nanoparticles (150.0 kGy) maintained higher antimicrobial activity than non-irradiated particles, e.g. being active toward S. aureus (16.0 mm). ZCFO is proposed as a candidate material for industrial and biomedical purposes.