- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
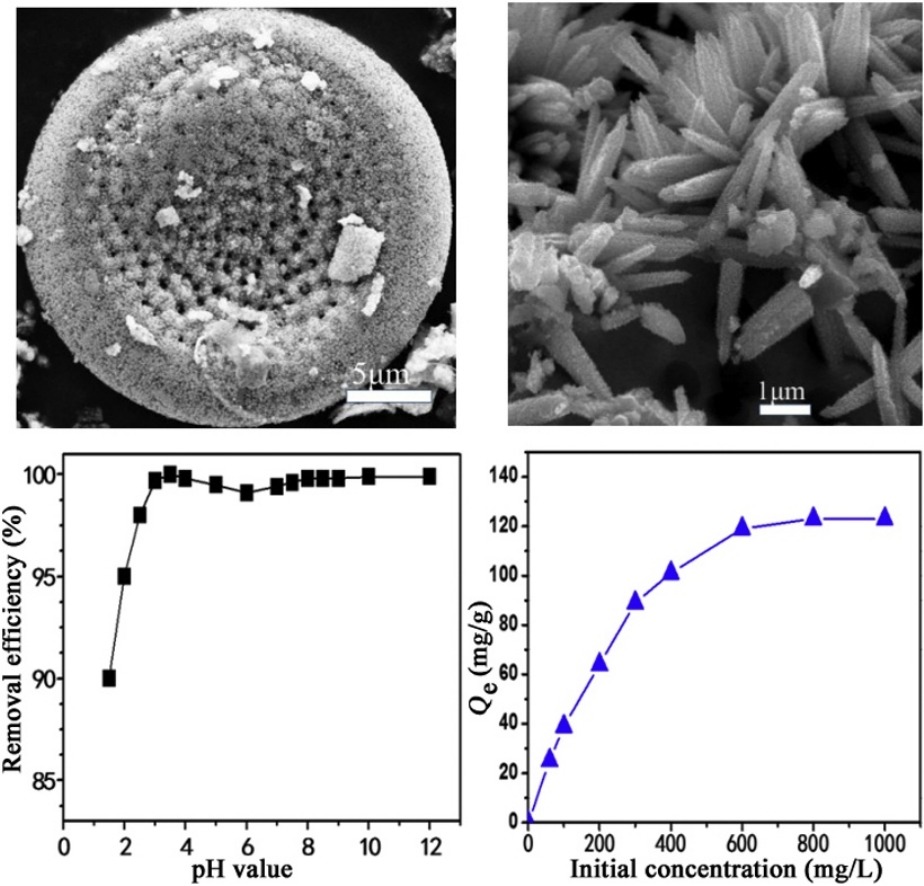
• Nb2O5 nanorod crystallized on diatomite substrate through a hydrothermal method.
• Specific surface area of Nb2O5-modified diatomite increased from 28 m2/g to 153 m2/g.
• The adsorption capacity increased consequently to 115 mg/g towards Cr(VI).
• Under UV light irradiation, surface adsorbed Cr(VI) could be photoreduced to Cr(III).
• The modified diatomite exhibited a synergistic effect of adsorption and photoreduction.
We report the design and synthesis of Nb2O5@diatomite composite materials. The composite materials are prepared by the hydrothermal conversion of raw diatomite and activated niobic acid powder in ammonium oxalate aqueous solution, with various hydrothermal reaction durations. The specific surface area of the diatomite modified by Nb2O5 nanorods reaches a maximum of 153 m2/g, which is almost five times higher than that of raw diatomite. Insights are gained into the function of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate and the mechanism of loading Nb2O5 on diatomite in the solution phase. The controllable growth dynamics allow the morphology and production of the Nb2O5@diatomite structure to be controlled. Adsorption experiments indicate that the diatomite modified by Nb2O5 nanorods is an effective adsorbent for quickly removing Cr(VI) from wastewater at room temperature. The maximum adsorption capacity is 115 mg/g. The Cr(VI) removal capacity is further improved under ultraviolet light irradiation, owing to the synergistic effect of surface adsorption and Nb2O5 photoreduction. The composite therefore has potential practical application.