- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
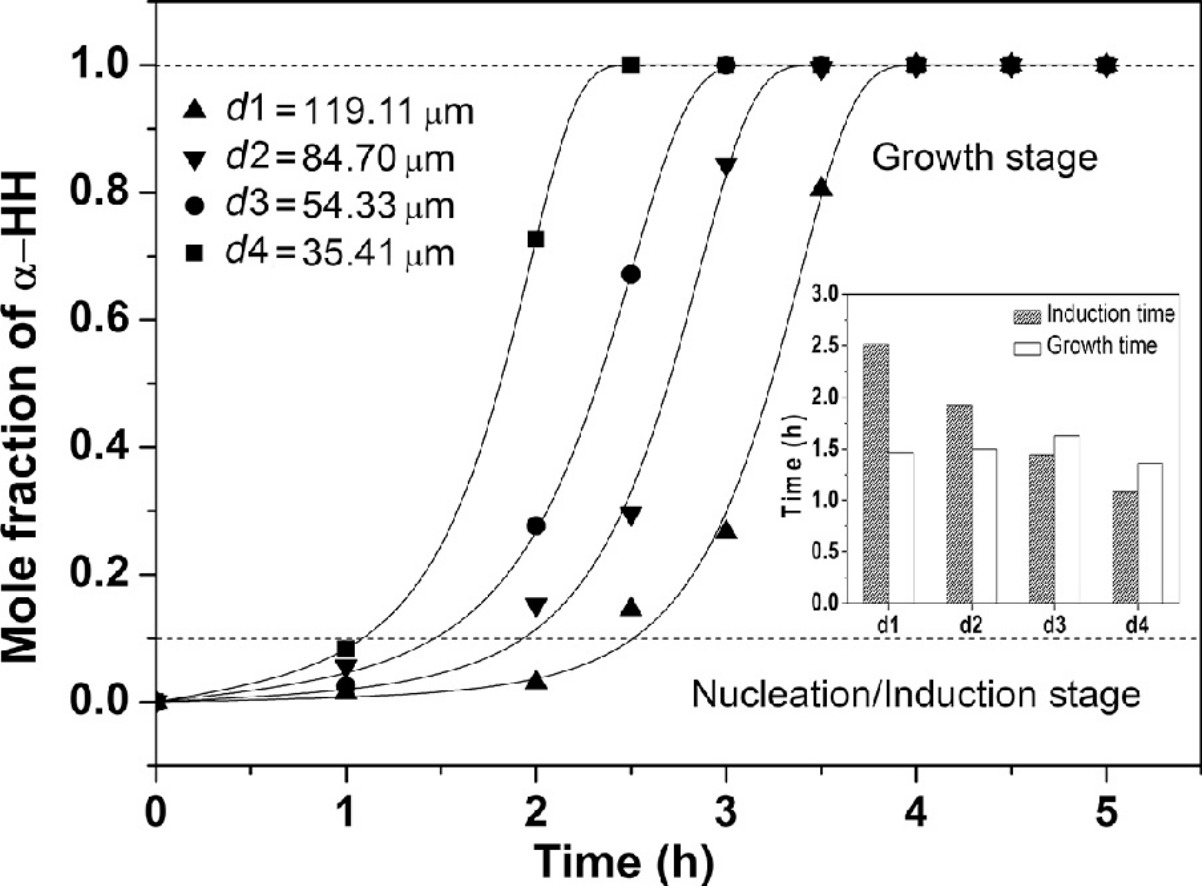
• Effect of particle size on transformation kinetics of FGD gypsum to α-HH was investigated.
• Particle size exerted significant effect on induction time but little effect on growth time of α-HH.
• Gypsum of smaller size provided more nucleation sites but can hardly enhance the driving force.
• The activation enthalpy decreased and activation entropy increased with decreasing particle size.
• The proportion of smaller α-HH crystals in products increased with decreasing parent crystal size.
The effect of particle size on the transformation kinetics of flue gas desulfurization (FGD) gypsum to α-calcium sulfate hemihydrate (α-HH) in calcium chloride (CaCl2) solutions was investigated to better guide value-added FGD gypsum use. Gypsum samples from different sources were sieved into several size groups, and their transformation rates were compared. The results showed that using FGD gypsum with a smaller particle size accelerated the transformation to α-HH. The size effect accelerated nucleation kinetics of α-HH rather than its crystal growth rate (that is, the thermodynamic driving force for the transformation changed little with particle size variation). Analysis using a kinetics model revealed that a smaller gypsum particle size lowered the overall activation energy barrier for the transformation. This is because the smaller gypsum particles had a larger relative specific surface area and thus provided more nucleation sites and crystalline defects to promote α-HH nucleation. A smaller particle size of FGD gypsum also gave a higher yield of fine α-HH particles because of the increased incidence of primary and secondary nucleation coupled with attrition. This paper indicates the transformation of FGD gypsum into α-HH could be effectively promoted by regulating FGD gypsum particle size.