- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
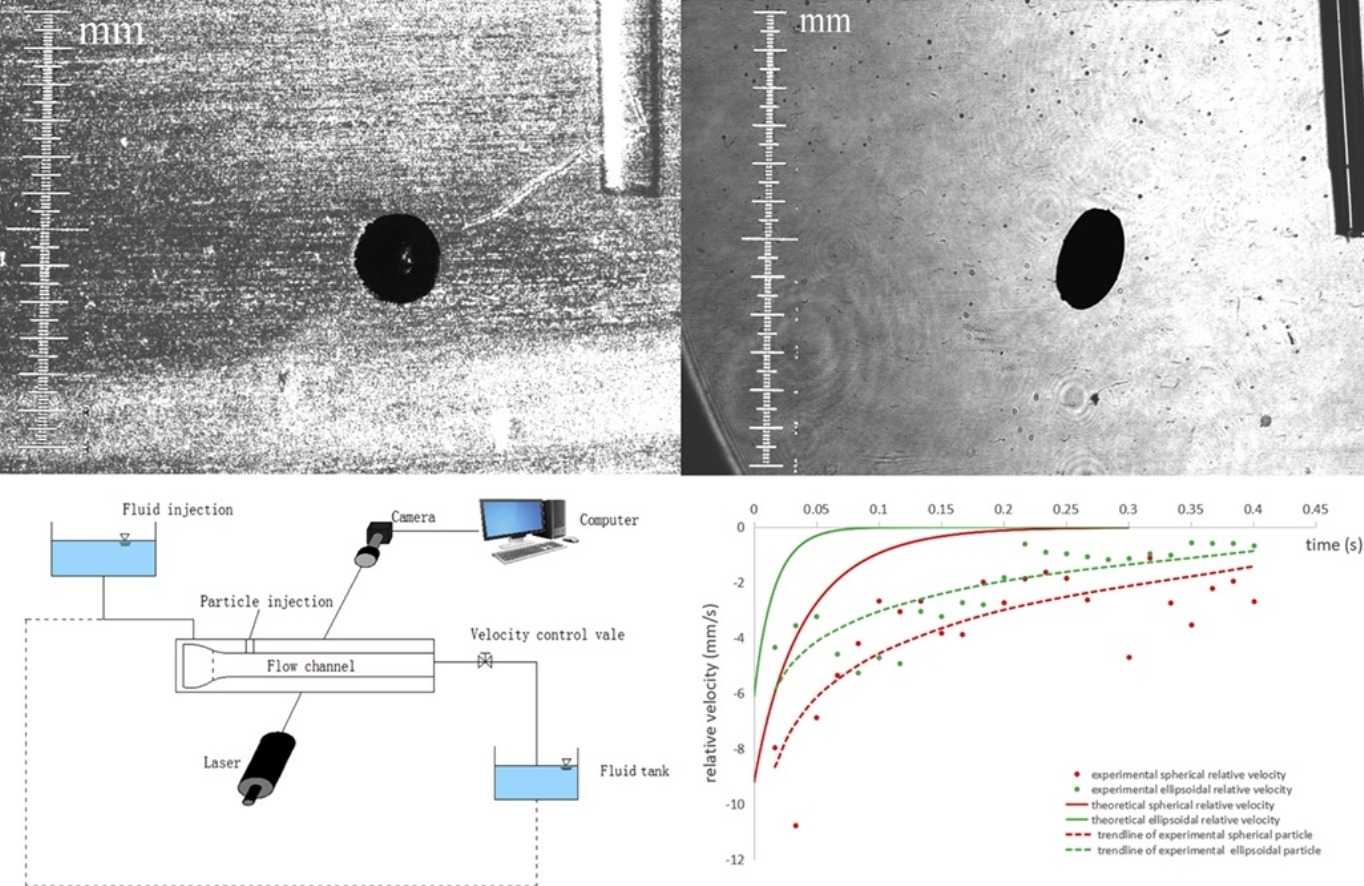
• Motion of an ellipsoidal particle in a horizontal laminar flow was studied experimentally.
• The entrained ellipsoidal particle achieved stable speed faster than a spherical one.
• The particle velocity was calculated based on modified BBO model.
A particle movement model for a horizontal laminar flow field was established in this study, using a modified Basset–Boussinesq–Oseen equation for multiphase fluid dynamics. The motion of ellipsoidal and spherical particles in this flow field was compared to determine the differences in entrainment of ellipsoidal versus spherical particles. Our theoretical results indicate that ellipsoidal particles move more rapidly and smoothly within the fluid than spherical particles under the same conditions. Moreover, this feature is enhanced, as the ellipsoidal degree of the particle increases. Based on a dimensional analysis, flow experiments were carried out to verify the behavior of ellipsoidal versus spherical particles in practice. Both our theoretical and experimental results show that ellipsoidal particles approach the fluid velocity more quickly than spherical particles. Future work would need to address effects of velocity gradients and rotation on particle behavior.