- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
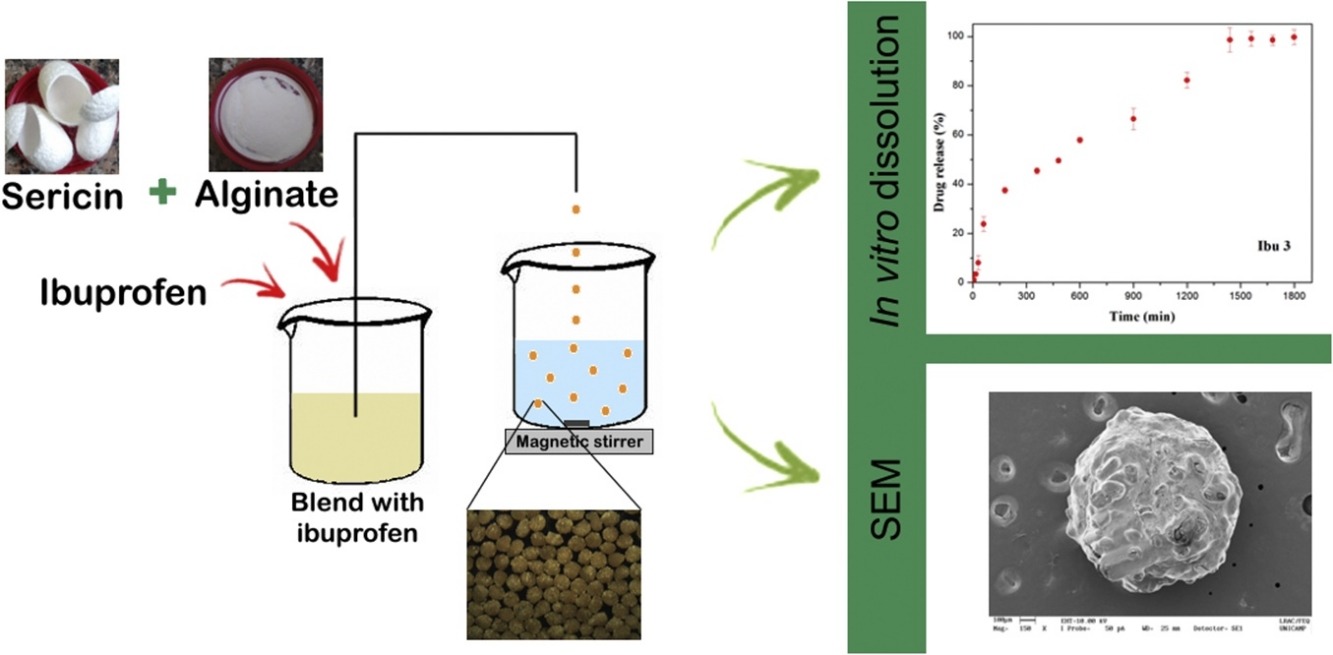
• Sericin/alginate blend was used as polymeric matrix for ibuprofen incorporation.
• Incorporation efficiency was improved by the addition of sericin as well as polyethylene glycol.
• Sustained drug release was reached by formulation with greater amounts of alginate.
• Sericin could contribute to improve homogeneity of particles size distribution.
A sericin/alginate blend was successfully applied as a matrix for incorporation of ibuprofen. This provided a sustained release formulation, which could improve the therapeutic efficacy of ibuprofen and patient adherence to treatment. Sericin increased the proportion of drug incorporated into the particles (i.e., the drug incorporation efficiency), with incorporation rates between 73.01% ± 1.70% and 94.15% ± 4.21%. Alginate affected the drug release, and the particles with the maximum alginate mass fraction tested (2.8%) showed sustained release through a dissolution mechanism, reaching equilibrium after about 1400 min. Analysis of the incorporation efficiency and the drug release time showed the best results were for formulations with a high alginate content. Scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction analysis were used for particle characterization to study the incorporation of ibuprofen. The particle size range was 0.80 ± 0.13 to 1.08 ± 0.11 mm. The size distributions of sericin-containing particles showed a good fit with the Gaussian model.