- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
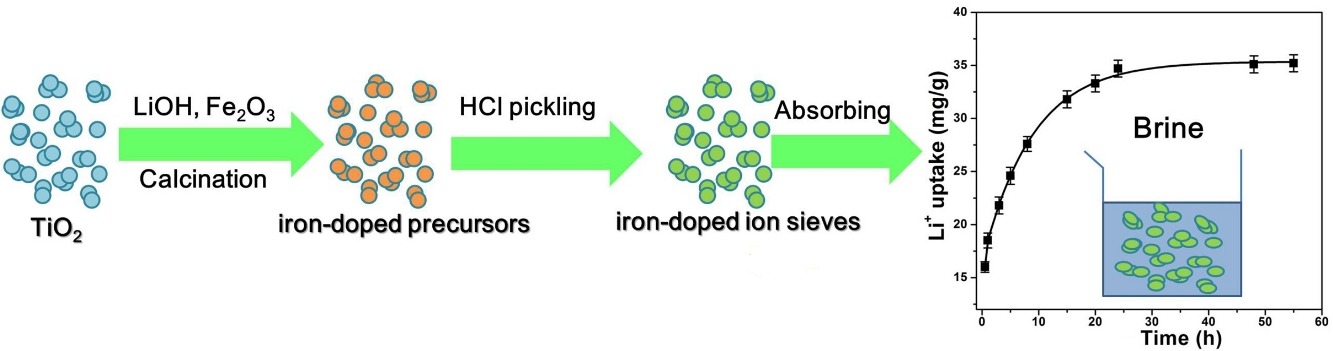
• Iron-doped lithium ion sieves were synthesized via solid-state reaction at 600 °C and Fe/Ti = 0.15.
• The synthesized sieves had Li+ adsorption capacity of ∼35 mg/g in brines.
• The synthesized ion sieves exhibited a high selectivity to Li+ and steady recyclability.
Iron-doped lithium titanium oxides were prepared via a solid-state reaction and transformed into lithium ion sieves by acid treatment. Scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy showed that Fe3+ was doped into the Ti–O lattice and Ti–Fe–O bonds were formed. Iron-doping improved lithium ion adsorption from brines. The saturated adsorption capacity of the iron-doped ion sieves in brine (Li+ 1.56 g/L, pH = 8.8) was 34.8 mg/g. Lithium ion adsorption fitted pseudo-second-order kinetic and Langmuir equations, indicating that lithium ion adsorption on iron-doped lithium ion sieves was chemical and predominantly monolayer. In addition, the iron-doped ion sieves showed excellent selectivity for lithium ion and good recyclability. These iron-doped ion sieves therefore provide effective lithium adsorbents for practical applications.