- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Ni/Sb-co-doped rutile pigment was prepared via mechanical activation and solid-state route.
• Mechanical activation favors the formation of new phases, i.e., brookite/rutile.
• Mechanical activation decreased rutile formation temperature.
• Mechanical activation improved the color performance of pigments.
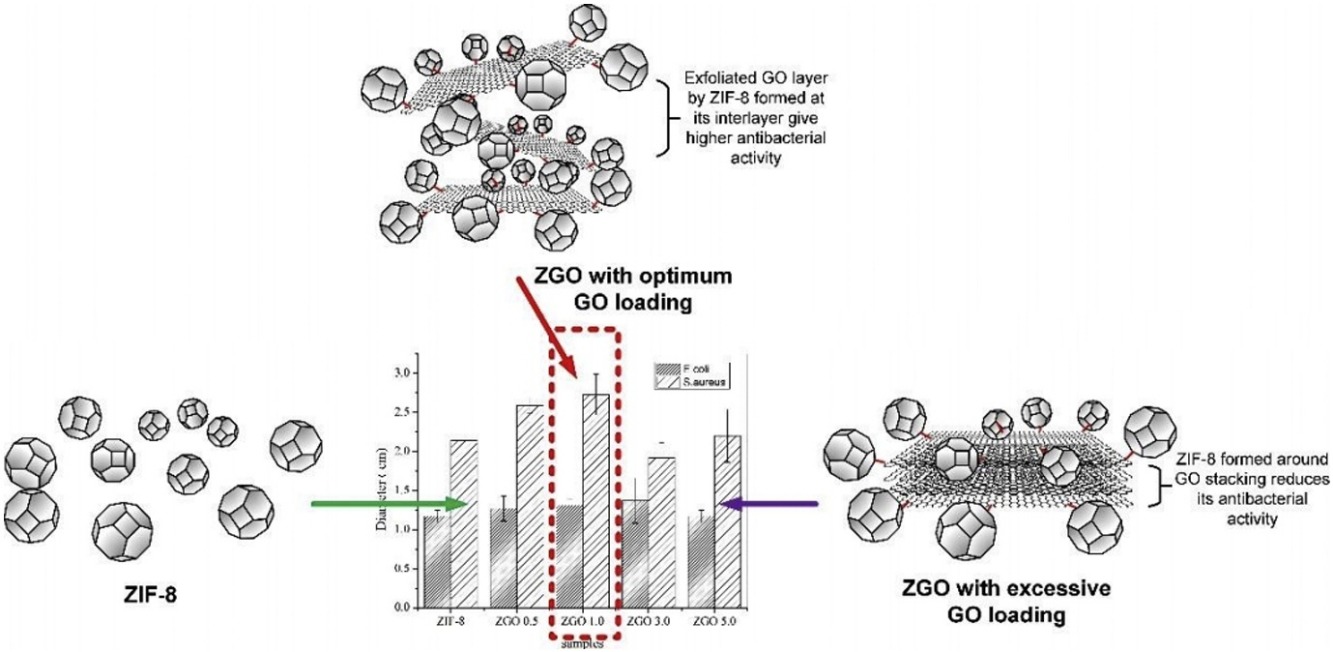
We report a rapid method for synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework 8 (ZIF-8)-decorated graphene oxide (GO) composites (ZGO) with good antibacterial properties. The ZGO composites were synthesized at room temperature with low GO to metal salt ratios. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, thermal gravimetric analysis, and surface area analysis. The characterization results show that ZIF-8 with a size of approximately 120 nm is successfully decorated on the surface of GO sheets with the host ZIF-8 framework maintained in the synthesized composite, but there is a significant reduction in the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area. The antibacterial activities of the samples against Escherichia coli ATCC 11229 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538 as model strains of gram-negative and -positive bacteria, respectively, were determined by disc diffusion and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) tests. ZGO-1.0 (1 wt% of ratio of GO to metal salt) shows the highest antibacterial activity with MIC values required to inhibit bacterial growth of E. coli and S. aureus of 5 times lower than those of pristine ZIF-8. Different antibacterial mechanisms are proposed based on field-emission scanning electron microscope images of the two bacteria after contact with the synthesized composite. Overall, owing to the simple synthesis, good stability, low chemical usage, and excellent antibacterial activity of the ZGO composites, they show great potential for application in the field of microbial contamination control.