- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
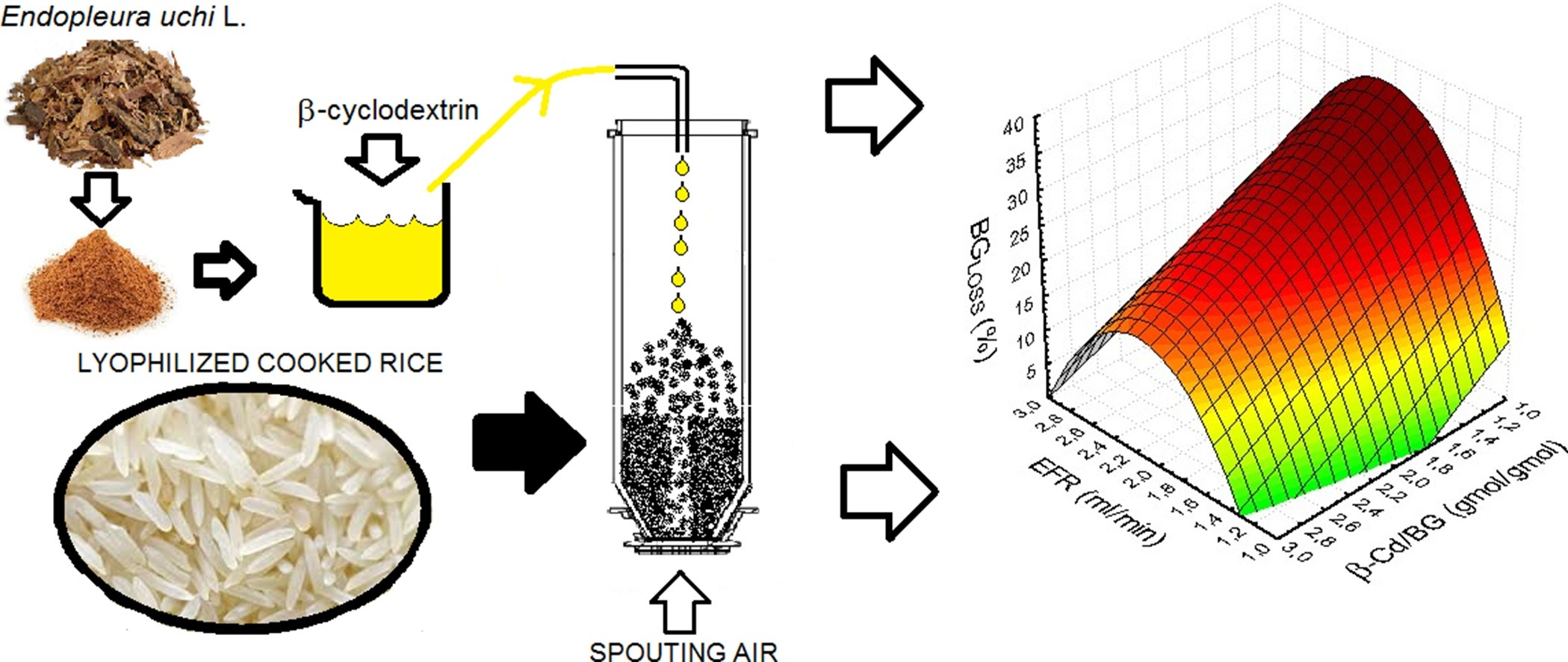
• β-cyclodextrin/bergenin inclusion complexes were incorporated on cooked rice in spouted bed.
• Multivariate approach was used to determine optimum conditions for improving product quality.
• Water solubility of bergenin in the product was almost twice that of pure bergenin.
Uxi (Endopleura uchi) is a plant from the Brazilian Amazon. It has many biological activities that are attributed to its main active component, bergenin (BG), which has low water solubility. The aim of this work was to obtain β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) inclusion complexes of uxi using lyophilized cooked rice as the solid substrate. The process was studied using a Box–Behnken design with the solution feed rate, molar ratio of β-CD to BG, and rice bed load as factors. These factors greatly affected the product bulk density, angle of repose, water content, and BG content, loss, and water solubility. The optimum process conditions determined using a desirability functions methodology were an extract feed rate of 1 mL/min, a ratio of β-CD to BG of 3:1, and a substrate load of 100 g. The predicted values under the optimum conditions were close to the experimental results of a water content of 5.8% ± 0.2%, BG content of 985.7 ± 15.4 μg/g, BG water solubility of 2230.2 ± 21.1 μg/mL, and BG loss of 1.2% ± 0.1%. These results confirm that spouted beds are an important tool for rapid, one-step preparation of pharmaceutical β-CD inclusion complexes in a solid form.