- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
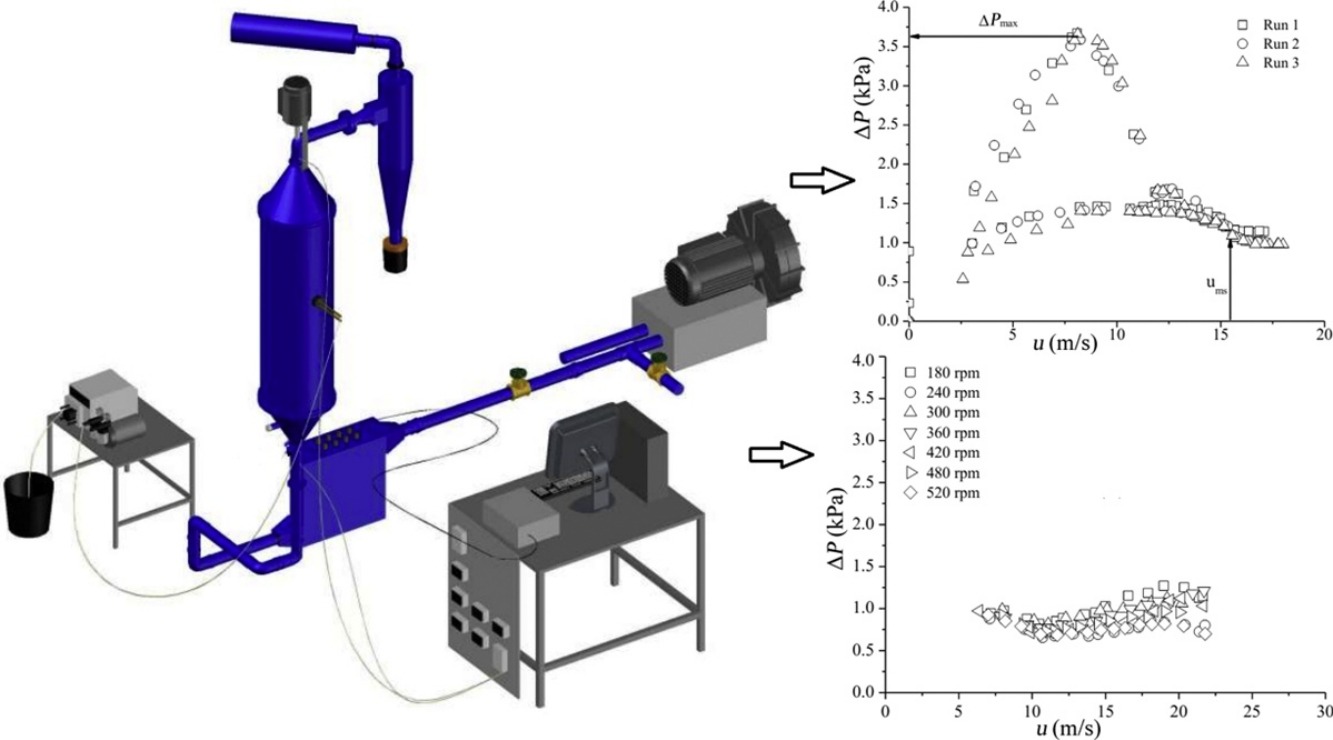
• A spouted bed was built to operate either with conventional or mechanically spouting.
• Conventional and mechanically spouted bed dynamics and drying performance were compared.
• Mechanically spouting was effective to dry diluted suspensions and coarse particles.
• Gas flowrate in drying solids was reduced by approximately 50% with a mechanically spouted bed.
• Conventional spouted bed performed better in drying liquid skimmed milk.
A contactor vessel was built to operate as either a mechanically or a conventional spouted bed for the purpose of analyzing the drying of pasty and granular materials under comparable conditions in both configurations. A classical conical–cylindrical spouted bed with a 60° conical base and an air inlet central orifice was modified to enable the switch by introducing in the vessel’s center an open helicoidal conveyor screw placed above the air inlet orifice. This screw is removable and conveniently returns the bed to its conventional spouted configuration. Experiments on drying solutions (calcium carbonate suspensions and skimmed milk) and granular materials (porous alumina particles) were performed for various bed parameter settings. The spouting pressure drop, outlet air temperature, and relative humidity were measured over time under different conditions. Mechanical agitation is proved effective in drying diluted carbonate calcium liquid suspensions and coarse porous alumina particles at an air velocity approximately 50% lower in comparison to drying in a conventional spouted bed. The conventional spouted bed performed better at drying liquid skimmed milk as the mechanical agitation combined with the axial inlet air flow is not effective in mitigating sticking and powder agglomeration in the bed when handling pastes of complex composition. Introducing mechanical agitation in the designed setup broadens the operating range of a conventional spouted bed with axial air flow in the inlet.