- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
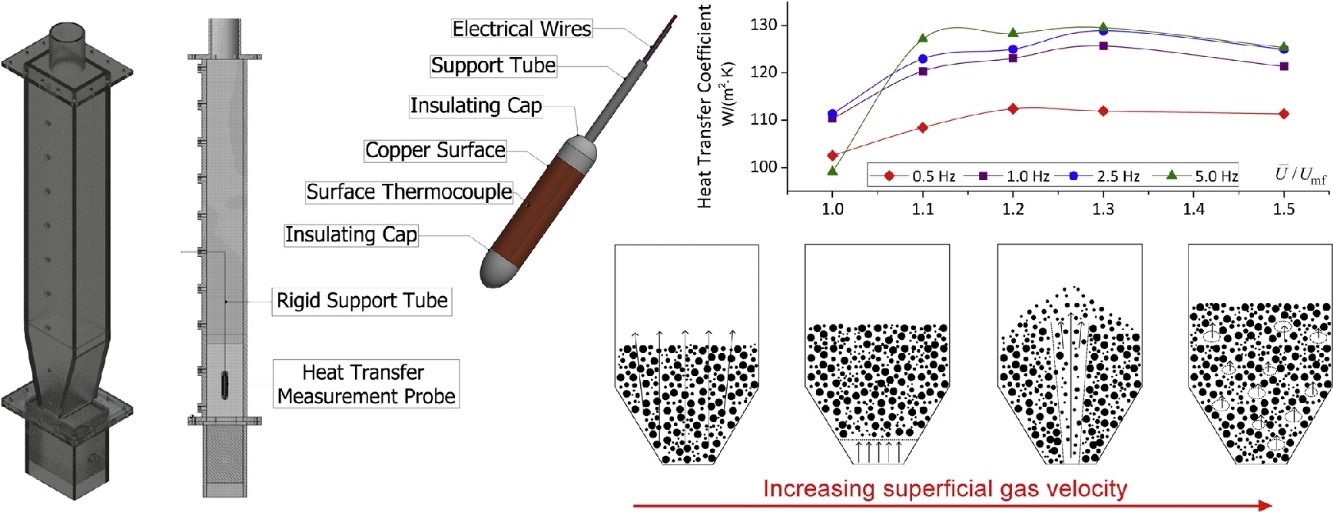
• Biomass was successfully fluidized in a tapered fluidized bed with pulsed gas flow.
• Flow pattern varied from channeling, slugging to bubbling at different flow rates.
• Weak gas pulsations led to core-annulus flow that increased lateral segregation.
• Maximum heat transfer coefficient was found around the natural frequency of pulsed fluidized bed.
• Smaller biomass particles exhibited faster heat transfer and smoother fluidization.
Bed-to-surface heat transfer of pure biomass particles in a pulsed fluidized bed with a tapered bottom section was investigated. Three biomass species — Douglas fir, pine, and switchgrass — were studied under various operating conditions. Their heat transfer coefficients were found to be closely associated with hydrodynamics dominated by gas pulsations. A higher superficial gas velocity generally yielded better gas–solid contact and higher heat transfer rates. A moderately increasing pulsation frequency promoted convective heat transfer of particles but also reduced pulsation intensity, leading to undesired flow behaviours such as channelling and partial defluidization. The study of the pulsation duty cycle revealed that, for cohesive particles, a smaller duty cycle was preferred to generate powerful pulsations to break up inter-particle forces. Moreover, a duty cycle increase allowed higher gas throughput as long as a suitable fluidization was maintained. The addition of finer particles to a coarse fraction increased particle mobility, and subsequently heat transfer, which also explained the higher heat transfer coefficients of switchgrass as it contained more fines compared with fir and pine. Experimental results in the tapered bed were also compared with those of non-tapered geometry where a 10%–20% increase in heat transfer was observed.