- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
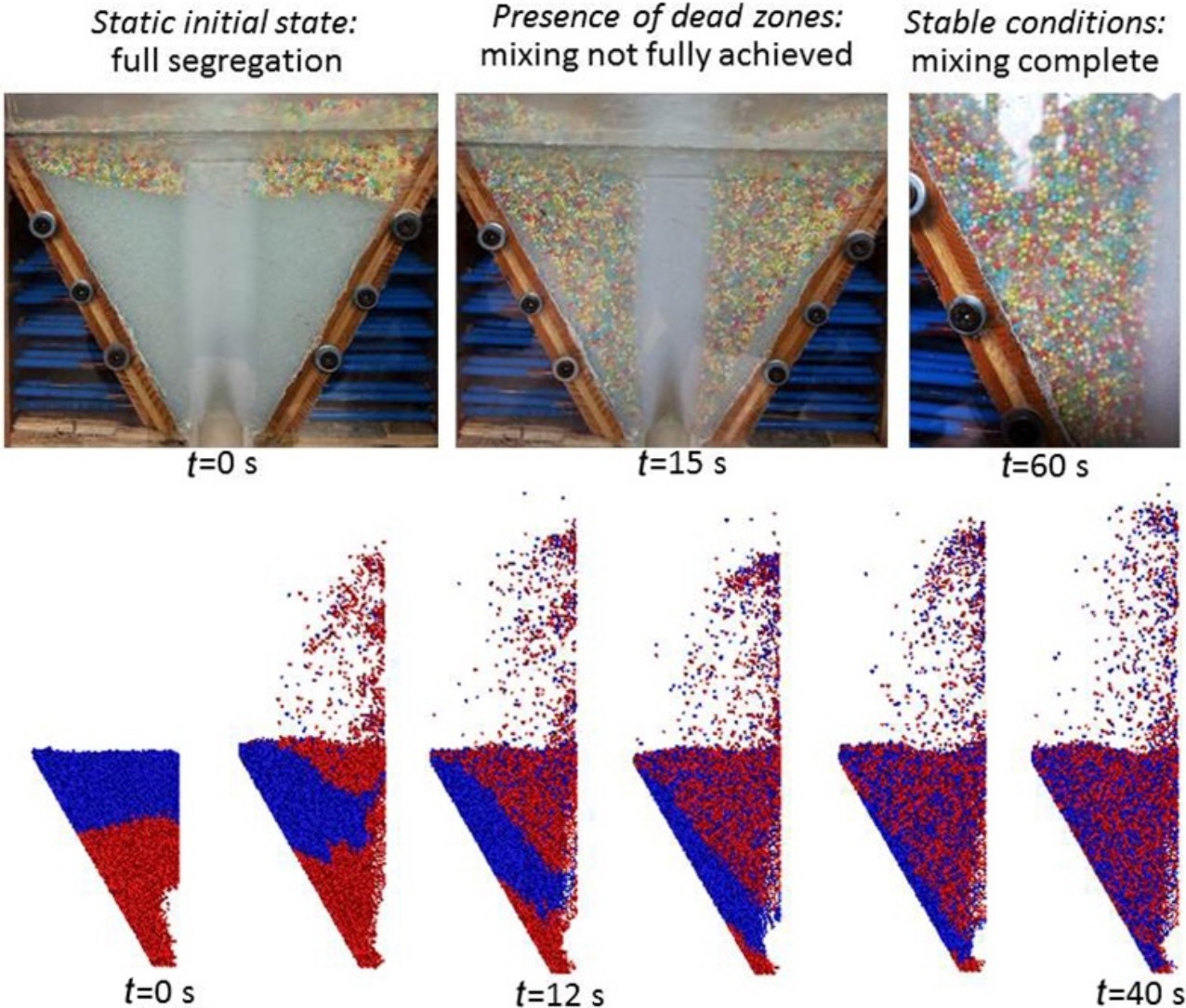
• Effects of binary mixture characteristics on segregation in spouted beds were assessed experimentally.
• Different density ratios of solids produced dead zones during start-up.
• Difference in diameter led to evident segregation phenomena.
• Highly irregular solids compromised the stability of the binary mixture system in a spouted bed.
• CFD–DEM model was able to reproduce segregation phenomena in a spouted bed.
From experiments, the influence of the physical characteristics of different binary mixtures of solids on the spouting regime of a pyramidal square-based spouted bed reactor is assessed. The applied methodology permits a more precise evaluation of the effects of the tested variables (diameter, density, sphericity) on the response variables (minimum air flows at which spouting begins and at which to maintain spouting conditions). The associated pressure drops along the bed of particles and the height of the formed fountain are analysed in each case. During the initial stages of fluidisation, binary mixtures containing different density ratios show dead zones. Segregation becomes more evident at large-size and high-density ratios. The lack of sphericity was found to be the main reason leading to blocking, channelling, and start-up problems when system failures occur. Nevertheless, the extent of segregation in all cases decreases with increasing the spouting velocity. In addition, a computational fluid dynamic model based on the discrete element method, previously validated for a single solid bed, is proposed as a tool to predict and evaluate potential segregation phenomena in binary mixtures. This model reproduced with high accuracy the encountered segregation phenomena. Its use may help define the technical limits inherent in the pyramidal spouted bed reactor.