- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Particle diameter distribution on the insulator surface with strong electric field was measured.
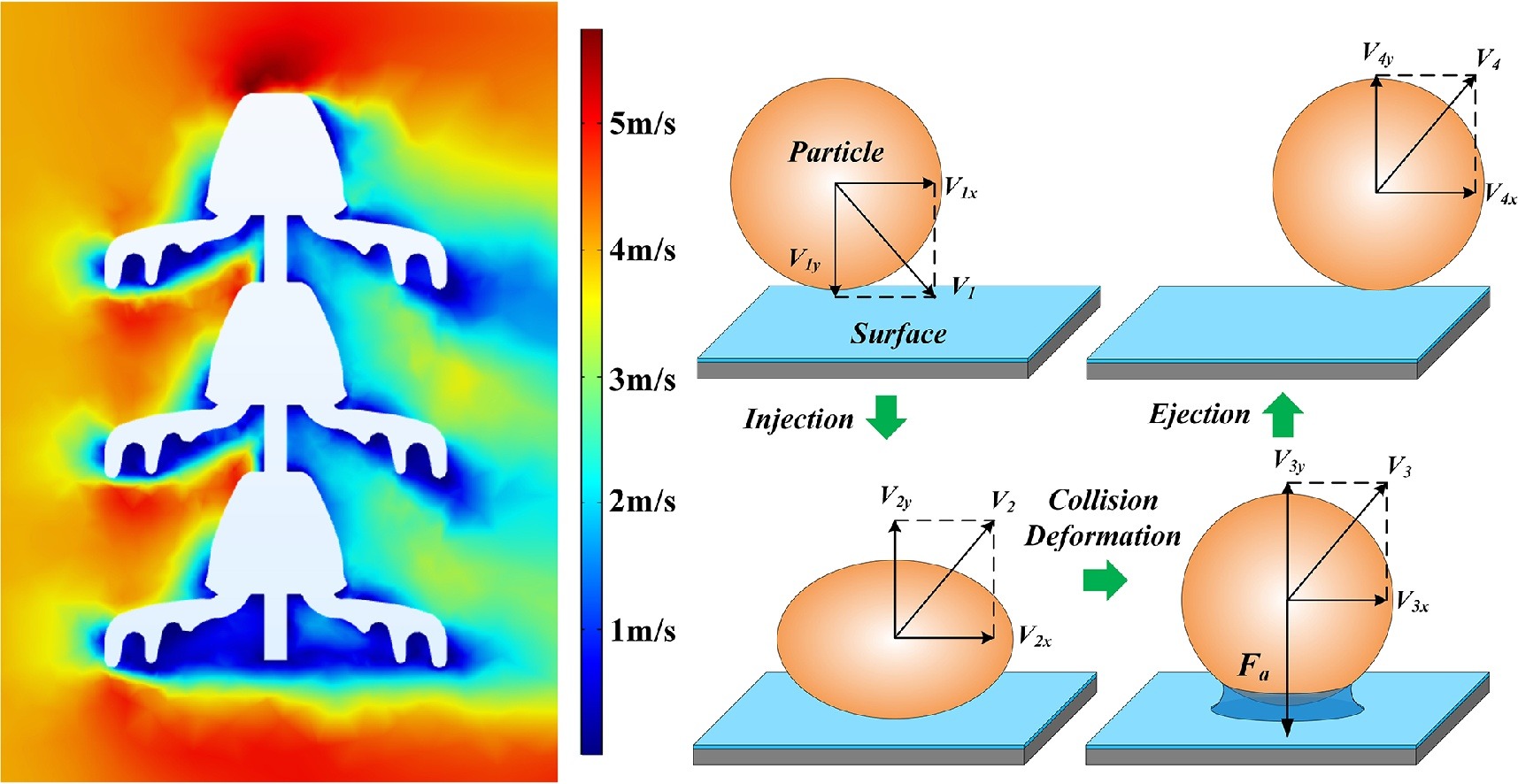
• A collision model was established in order to analyze the trajectory of particles.
• Relative humidity and wind speed have an obvious effect on the adhesion of particles.
• The particle diameter distribution of adhered particles shows significant concentration.
• The higher relative humidity is, the more the adhered particles are.
Insulators on high-voltage transmission lines are almost the only man-made structures on the Earth’s surface intended for long-term operation under strong electric fields. After samples of natural contaminant particles were collected from insulator surfaces in China, it was found that the particle diameter distribution (PDD) was mainly concentrated in the 5–50 μm range. To analyze the statistical characteristics of these particles, this work studies the physical processes of particle collision and adhesion using the theories of hydrodynamics and collision dynamics. The physical model considers coupling of the fluid field and the electric field, introduces an adhesion criterion, and establishes a particle and surface collision model. The effects of relative humidity, wind speed, aerodynamic shape, electric field type, and electric field strength on particle adhesion were analyzed. The results show that the relative humidity and wind speed have very significant effects and the influences of the electric field type and the electric field strength are obvious, but the influence of the aerodynamic shape is relatively weak. The simulation results support the statistical characteristics determined in this work. The physical model established here provides reference values for study of the adhesion characteristics of particles on surfaces under electric fields.