- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
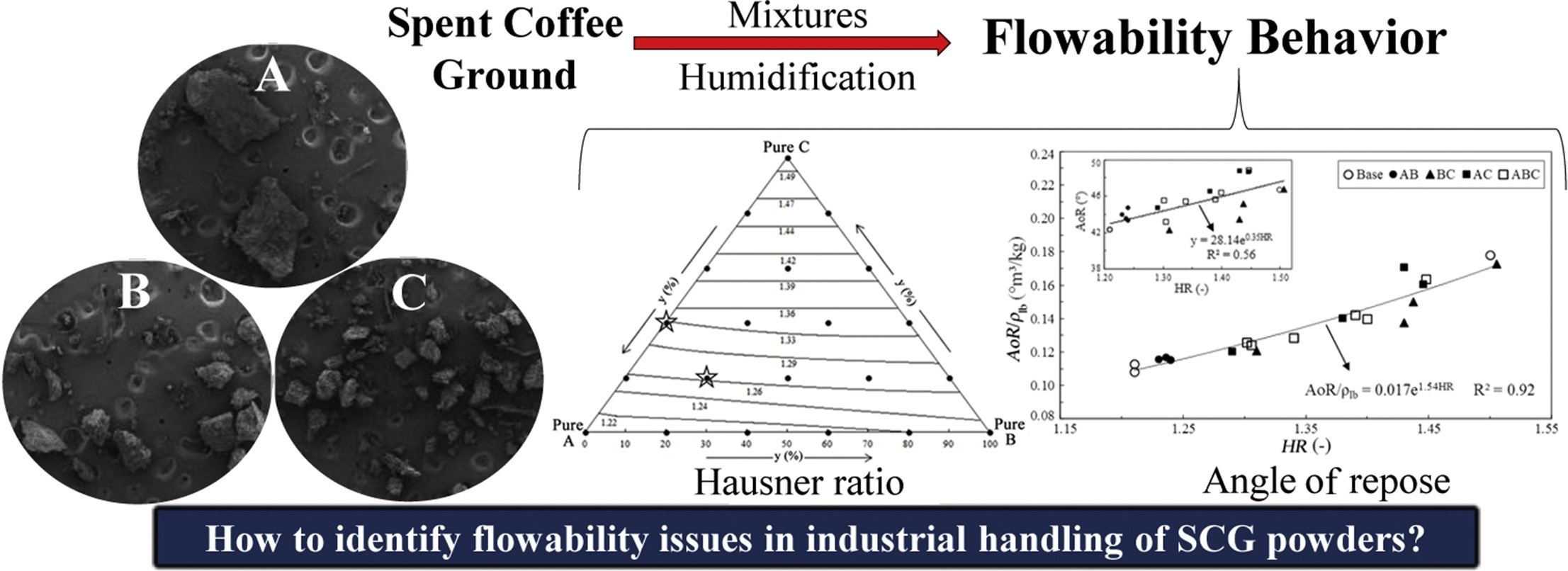
• Spent coffee grounds (SCG) have worse flowability than other biomasses.
• Powders with mean diameters <350 μm and mixtures with >40% fines have poor flowability.
• Dry and wet SCG have similar flowability up to a water content of 50%.
• This knowledge could be used in process design of industrial plants handling SCG.
The main use for spent coffee grounds (SCG) produced in the soluble coffee industry is thermal energy generation in the industry itself. The SCG are processed using operations that are strongly dependent on powder flow behavior. In this study, we evaluated two classical flowability indices of non-consolidated SCG powders: the angle of repose (AoR), and the Hausner ratio (HR). The influences of the mean particle diameter, particle size distribution (PSD), and water content on the AoR and HR values of SCG were analyzed for powders with a mean particle size range of 225–550 μm. For powders with a mean particle size close to 350 μm and for mixtures containing more than 40% fine particles, the HR (>1.35) and AoR (>45°) values were characteristic of poor flowability. The AoR was sensitive to the powder PSD, and powders with similar mean particle sizes had higher AoR values when the PSD was larger. For powders with water contents up to 50%, the flowability indices were not greatly affected by the water content. A modified linear-mixture packing model was used to predict the packed bed void fractions for binary and ternary mixtures of the three base powders. The model was used to construct a ternary diagram to estimate the HR values of the mixtures. An equation was fitted to correlate HR and AoR. The proposed diagram and the equation provide insight into flow behavior and could be used for process design of industrial plants that handle SCG.