- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
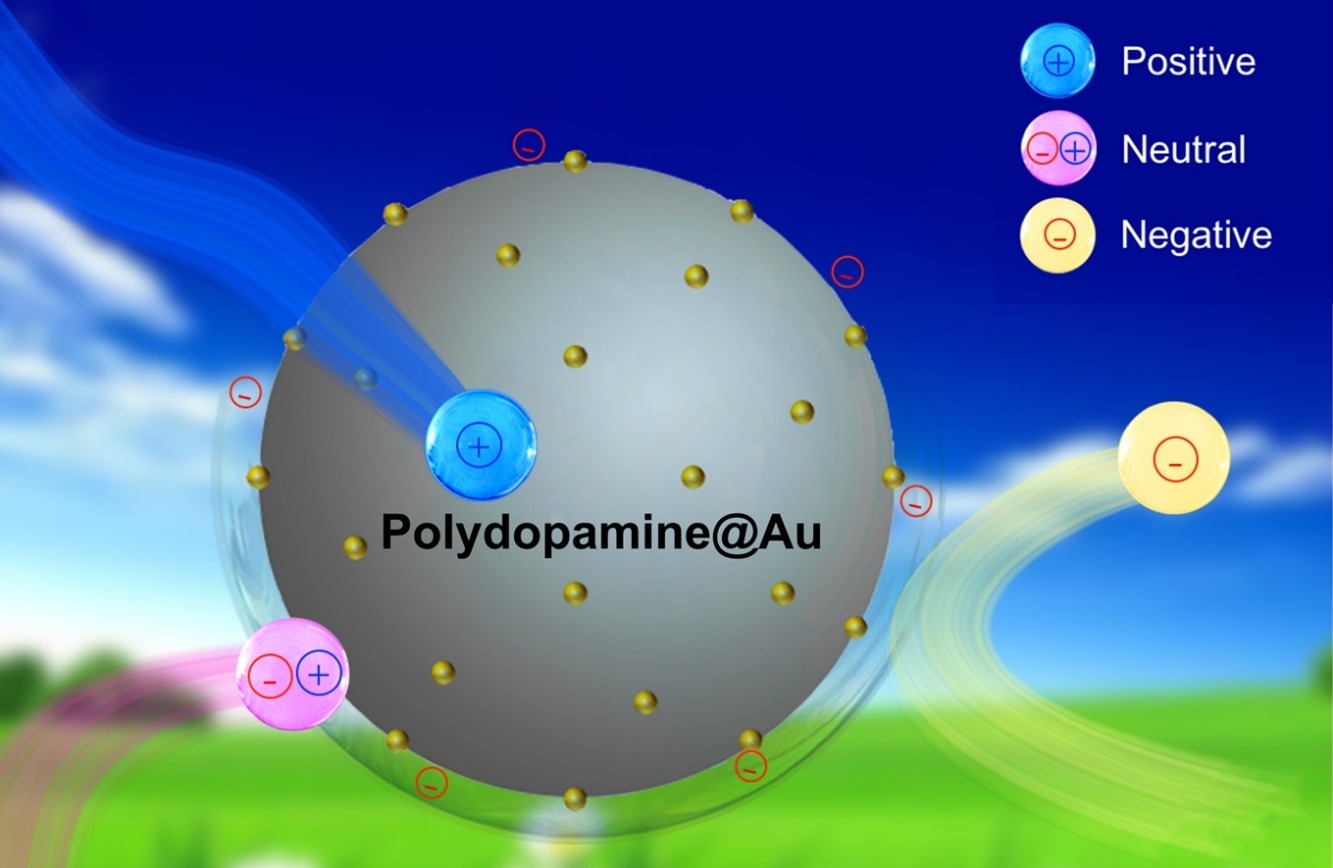
• In situ reduction of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) on polydopamine (PDA) formed PDA@Au particles.
• This approach increased Au content and enhanced stability of AuNPs attached to PDA.
• Different catalytic mechanisms of PDA and PDA@Au particles are proposed.
• Charge-dependent catalytic behaviors of the particles were investigated.
The versatile catechol unit of polydopamine (PDA) endows this molecule with a broad ranging adhesive properties and reducibility. We prepared free-standing PDA particles by a simple self-polymerization and these particles served as both an effective reductant and scaffold for a hybrid catalyst. The raspberry-like nanocomposites featured a high density of AuNPs uniformly deposited on PDA particles (PDA@Au). This system was prepared in-situ with assistance from the active catechol and amine groups of the PDA particles. To quantify the effect of the PDA carriers, we studied the catalytic activity of the PDA and PDA@Au particles. The PDA particles showed a pronounced charge-dependent catalytic activity for reduction of cationic methylene blue, negatively-charged 4-nitrophenolate, and zwitterionic rhodamine B in the presence of borohydride, whereas PDA@AuNPs showed catalytic activity with a less pronounced charge-dependence of the catalytic efficiency of the AuNPs. The PDA particles served as a redox mediator and adsorbent accelerator in degradation of the dyes owing to its unique chemical structure.