- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
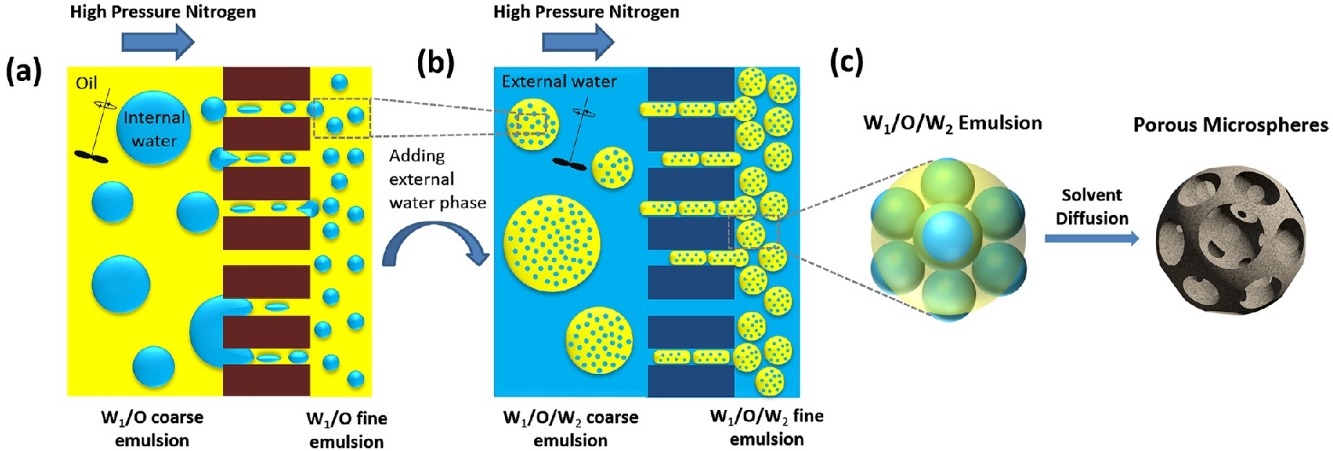
• Uniform W/O/W emulsions were generated by two-step premix membrane emulsification.
• The porous microsphere particle and pore sizes were precisely adjustable.
• These porous microspheres have potential application as chromatographic media.
A scalable and versatile strategy was developed for the fabrication of uniform polymeric microspheres with controllable interconnected porous structures. Uniform water-in-oil-in-water emulsions with linear poly(methyl methacrylate–glycidyl methacrylate) in the oil phase were generated by two-step premix membrane emulsification and used for constructing the microspheres. During the emulsion solidification process, internal water droplets were packed densely together, forming a thin oil film between the internal and external water phases. After solvent diffusion, the thin film can be ruptured and pores can be templated from the internal water droplets to form interconnected porous structures. Membranes with various pore sizes were obtained. The osmotic pressure and Laplace pressure balance were used to control the porosity and pore size precisely. The proposed method enables the fabrication of functional polymeric microspheres with uniform and controllable porous structures and particle sizes. This improves their performance and broadens the scope of their applications, especially in chromatographic separation.