- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
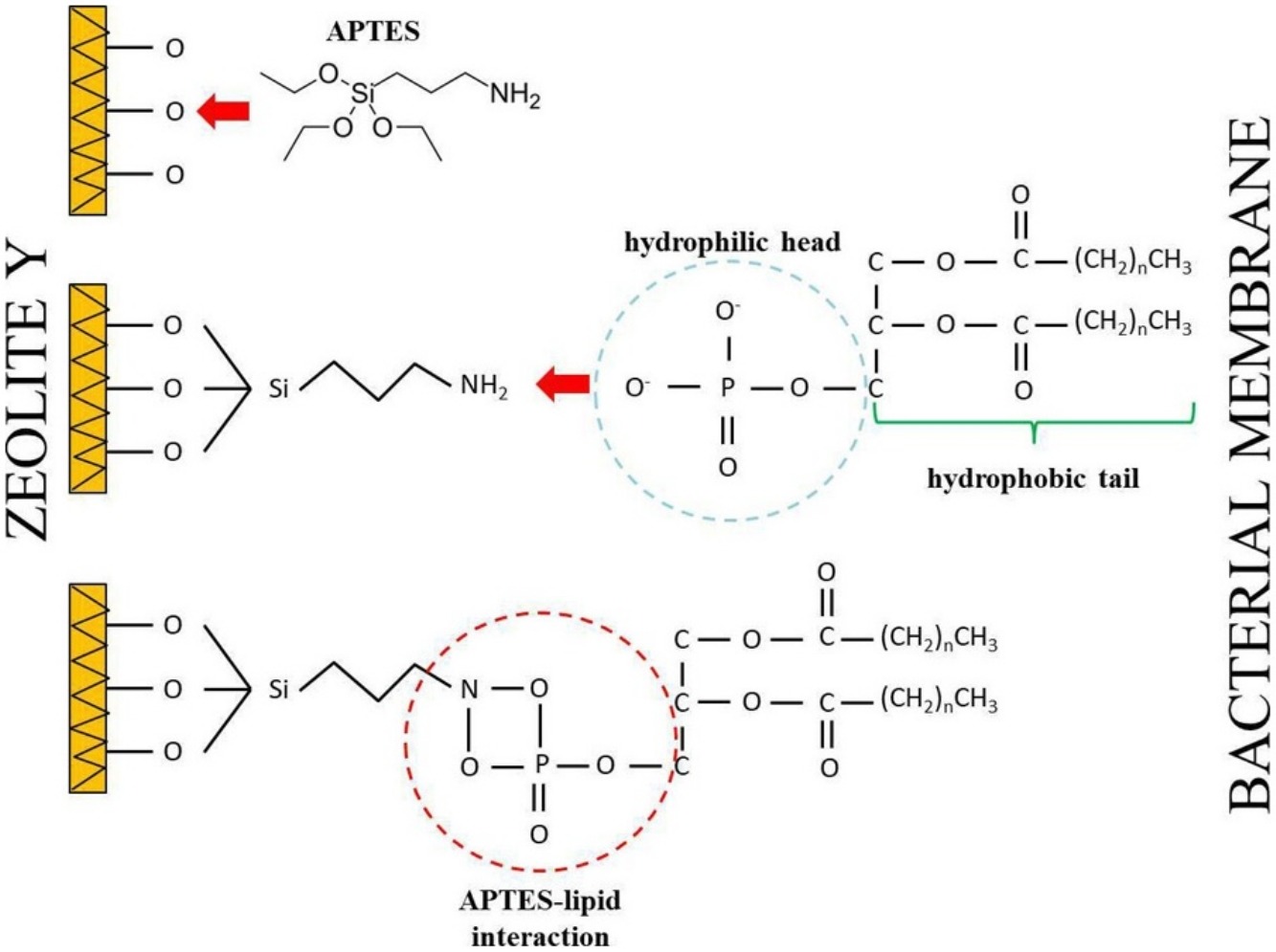
• Zeolite Y was amine-functionalised with (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane (APTES).
• APTES-zeolite Y showed antibacterial activity against various ATCC bacteria.
• High amounts of APTES on zeolite Y were cytotoxic against human fibroblast cells.
• High amounts of APTES on zeolite Y reduced cellular wound healing activity.
The antibacterial activities, cytotoxicity, and wound healing of amine(3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES))-functionalised zeolite Y against normal human fibroblast cells were studied. The characterisation of unmodified and amine-functionalised zeolites Y (Z, ZA 0.04, ZA 0.4, and ZA 0.6) by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffraction, and energy dispersive X-ray analysis proved that the APTES molecules were grafted onto the zeolite Y surface without distorting its framework structure. All amine-functionalised zeolite Y samples possessed antibacterial activities against several ATCC bacteria that were correlated with the increased amount of APTES on the zeolite Y surface. Conversely, when a higher concentration of APTES was grafted on the zeolite Y, higher cytotoxicity was observed against the fibroblast cells. Although the ZA 0.6 sample (zeolite Y functionalised with 0.6 M of APTES) had higher antibacterial activity, it was cytotoxic to the cells. Therefore, the selection of an antibacterial agent for human treatment purposes must also consider its cytotoxicity effect against human cells to ensure it is biocompatible.