- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
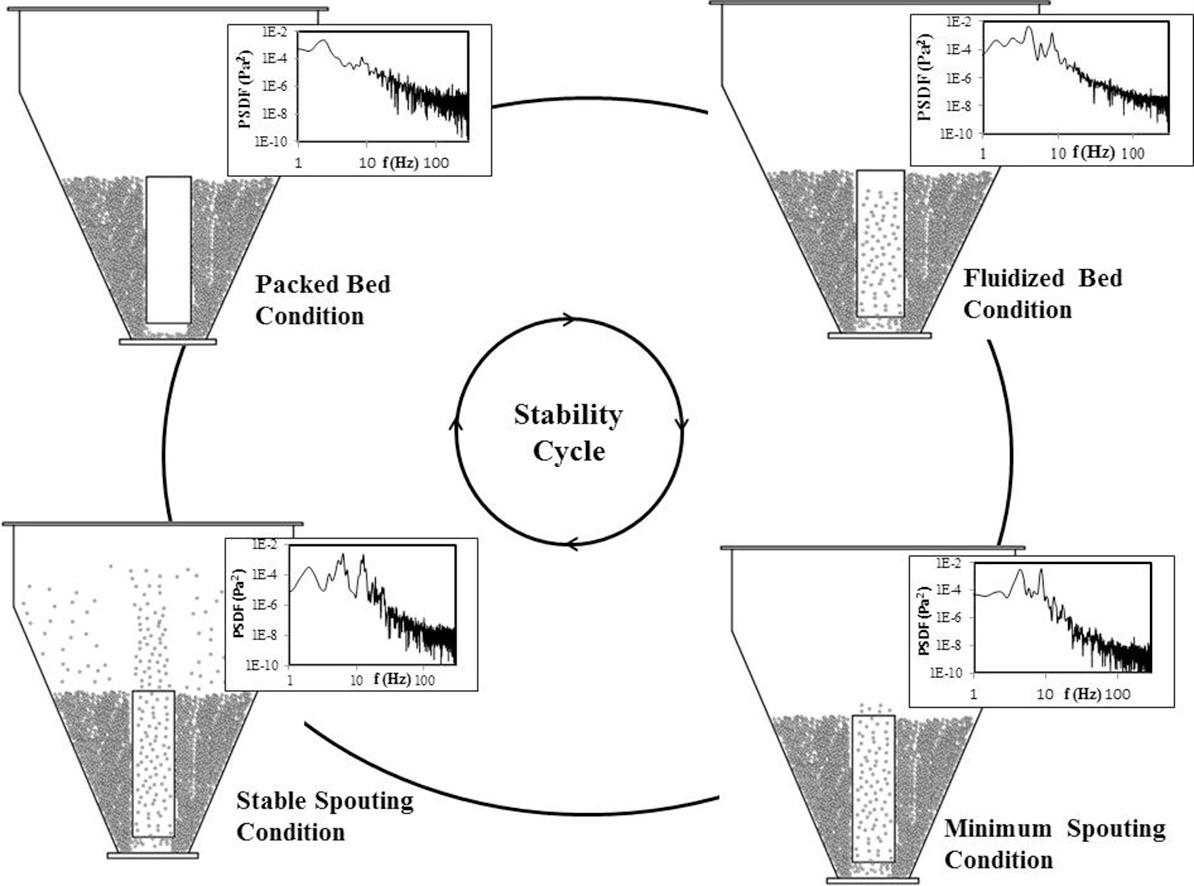
• Three different flow regimes were detected using PSDFs of pressure fluctuations.
• Slow movement of pellets in annulus lies in the frequency ranges less than 5 Hz.
• Bulk movement of pellets inside the draft tube occurs at the frequencies at about 8 Hz.
• Horizontal movement of pellets through entrainment zone has the frequency at about 13 Hz.
• A new correlation was proposed predicting minimum spouting velocity of a Würster apparatus.
The flow of pharmaceutical pellets in a Würster fluid bed (WFB) was characterized by a frequency domain analysis of pressure fluctuations. Pellets with a diameter of 0.780 mm and density of 1.225 kg/m3 were used in the experiments. Different flow structures were identified in the bed, including bulk movement of pellets in the annulus (f < 5 Hz), bulk movement of pellets inside the draft tube and bulk horizontal movement of pellets through the entrainment zone (5 < f < 15 Hz), and clustering (15 < f < 145 Hz). The minimum spouting velocity was also measured experimentally. Effects of bed height, distance of the entrainment zone, and distributor hole pitch on minimum spouting velocity were investigated. It was found that the minimum spouting velocity increased with increasing bed height and distance of the entrainment zone while it decreased with increasing distributor hole pitch. A correlation was developed for estimating the minimum spouting velocity in WFBs containing pharmaceutical pellets. The correlation fit the experimental data satisfactorily. Studying the WFB hydrodynamics and determining the minimum spouting velocity provides information that can be used to properly design, operate, and scale up such systems.